Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

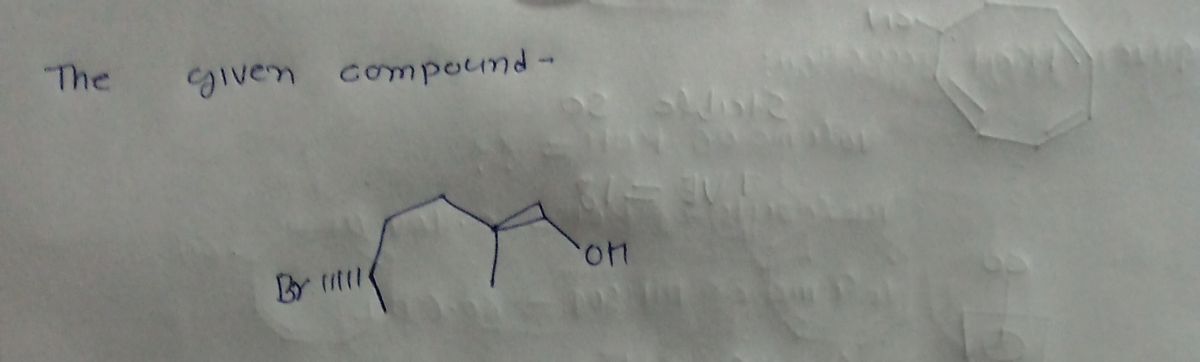
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts the structural formula of a chemical compound, specifically 4-bromo-2-hexanol.
**Structure Description:**
- The main carbon backbone consists of a six-carbon chain (hexane).
- A hydroxyl group (-OH) is attached to the second carbon, indicating that the compound is an alcohol. This defines the position for the “2-hexanol” part of the name.
- A bromine atom (Br) is bonded to the fourth carbon in the chain, indicated by the lines that represent the stereochemistry at that carbon.
**Chemical Features:**
- **Alcohol Functional Group:** The presence of the -OH group classifies this compound as an alcohol.
- **Bromine Substituent:** The Br atom indicates a halogenation at the fourth position.
The representation is a common way to illustrate organic molecules, highlighting both the arrangement and specific bonding of atoms within the compound.

Transcribed Image Text:**Question Prompt:**
1. Name the compound (hidden text).
2. Write the structural formula of the enantiomer. (hidden text)
---
**Explanation:**
The text above presents two chemical tasks typically encountered in organic chemistry:
1. **Naming the Compound:**
- The task involves identifying the compound based on chemical structure or molecular formula. This information has been redacted in the image, which usually challenges learners to apply IUPAC nomenclature rules for organic compounds.
2. **Writing the Structural Formula for the Enantiomer:**
- An enantiomer refers to one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other and are not superimposable. Writing the structural formula of an enantiomer involves reversing the configuration around the chiral center(s) of the given compound. This skill is crucial for understanding the behavior of chiral molecules in biological systems.
Understanding and performing these tasks are essential skills for students studying organic chemistry or related fields.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Concept: first we will determine the stereochemistry of each stereo center than we will find enantiomer.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY