Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
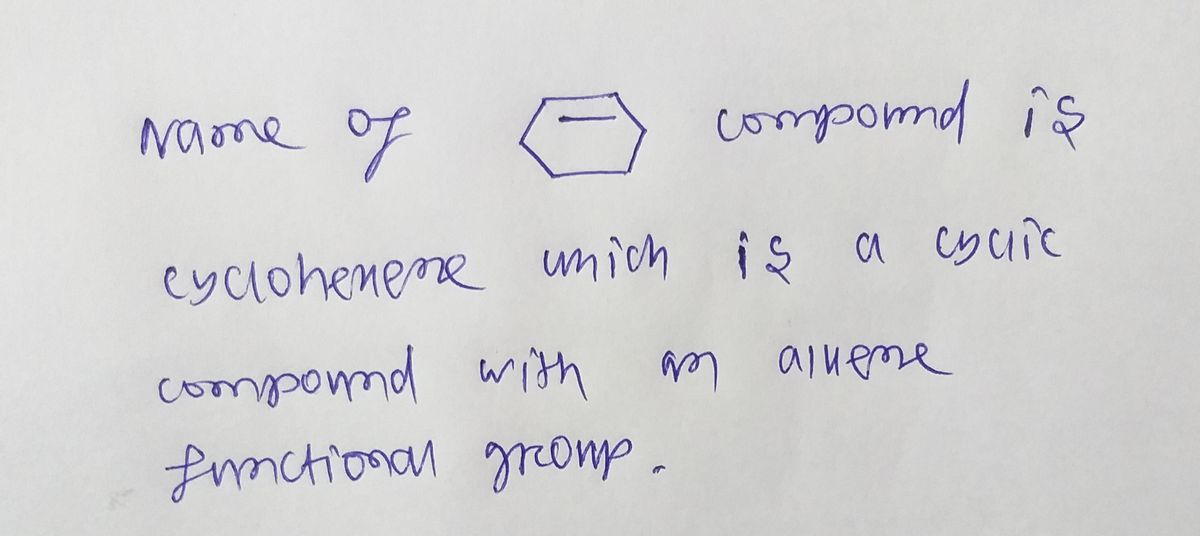
How do I draw the product ? please help

Transcribed Image Text:This image depicts a two-step bromination reaction mechanism involving a cyclohexene molecule and bromine (\( \text{Br}_2 \)).
**First Diagram:**
- A cyclohexene molecule is represented with a double bond.
- A bromine molecule is shown approaching the double bond.
- Two curved arrows indicate the electron movement: one from the double bond to one of the bromine atoms, and another from the bromine-bromine bond to the opposite bromine atom.
**Second Diagram:**
- The result of the electrophilic addition is shown.
- A cyclic bromonium ion intermediate is formed, where the bromine is bonded to two carbon atoms, creating a three-membered ring.
- The bromine now carries a positive charge (\( \text{Br}^+ \)).
- The negatively charged bromide ion (\( \text{Br}^- \)) is shown with a lone pair, prepared to open the bromonium ring.
- A curved arrow shows the lone pair of the bromide ion attacking the more substituted carbon of the bromonium ion.
This reaction forms part of a typical mechanism for the electrophilic addition of halogens to alkenes, illustrating how bromine adds across a carbon-carbon double bond.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY