Introduction to Organic Chemistry
The field of chemistry which deals with the studies of reactions, structures, and properties of organic compounds that comprise carbon bonded through covalent bonding is organic chemistry. The studies regarding the structure of organic compounds could be determined with the help of structural formulas. In order to know about the behavior of organic compounds, a study on the properties has to be done. Both physical properties and chemical properties, the origin of chemical reactivity come under the study regarding the properties of organic compounds. The chemical preparation of polymers, drugs, natural products, and the study of separate organic molecules in the lab come under the study of organic reactions.
Vinyl Group
Vinyl group is the name given to the functional group of -CH=CH2. It can be seen as an ethene molecule with one less hydrogen in number. Hence it is also called as ethenyl group at times.
Straight Chain Hydrocarbons
The requirement to identify each compound needs a richer number of words than informative prefixes like n and iso. The identification of organic molecules is made easier by the use of systematic nomenclature schemes. The organic chemistry nomenclature has two types: traditional and systematic. Common names arise in many forms, but share the characteristic that a link through name and form is unnecessary. The name that matches a certain structure clearly must be remembered as knowing a person's name. In contrast, systemic names, including an overall common set of laws, are locked specifically to the chemical structure.
Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
Following are few examples of alkenes with their general molecular as well as their structural formulas:
Conjugated Compounds in Organic Chemistry
The delocalization of electrons in a molecule is called conjugation in organic chemistry. This delocalisation process of electrons leads to the shortenings or elongations of chemical bonds, but at the same time it causes changes in the chemical properties in conjugated molecules as compared to the non-conjugated ones. For example, conjugated molecules absorb light at longer wavelengths.
Alpha Carbon And Alpha Protons
The carbon directly attached to the functional group in an organic molecule is referred to as the alpha carbon and the hydrogen attached to an alpha carbon are termed as the alpha hydrogens or alpha protons. These alpha carbon atoms and alpha hydrogen atoms are of importance because they undergo certain characteristic reactions in organic chemistry.
Which of the attached molecules can hydrogen bond to another molecule like itself? Which can hydrogen bond to water?

Since we only answer upto 3 sub-parts we'll answer first 3. Please resubmit the question and specify the other sub-parts you'd like answered.
Hydrogen bond is a chemical bond that is formed between the hydrogen and one electronegative atom.
For hydrogen bonding 2 conditions are necessary:
A hydrogen atom must bonded to electronegative atom.
Another atom must have free electron pairs to which the hydrogen atom can bond.
a)
Compound:
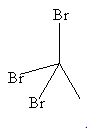
CBr3CH3
No hydrogen in this molecule is bonded with electronegative element. All three such atoms bonded to carbon. So, not any hydrogen is available for hydrogen bonding.
Bromine has free electron pairs but not too much electronegative and so its orbitals are too large for stable hydrogen bond formation.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images









