Barbados currently uses a fixed exchange rate regime. If the central back were to increase the money supply, what impacts would it have on the economy? Use a diagram to explain your answer.
Barbados currently uses a fixed exchange rate regime. If the central back were to increase the money supply, what impacts would it have on the economy? Use a diagram to explain your answer.
Answer:
Introduction:
In the fixed exchange rate regime, official intervention (by monetary authorities or government) is used to maintain the exchange rate at a particular value.
Explanation:
Suppose Initially, the economy is in equilibrium in the goods market (IS curve), money market (LM curve), and external sector (Balance of Payment curve). The domestic interest rate is equal to the global interest rate. There is no capital mobility.
Graphical presentation of the initial situation:
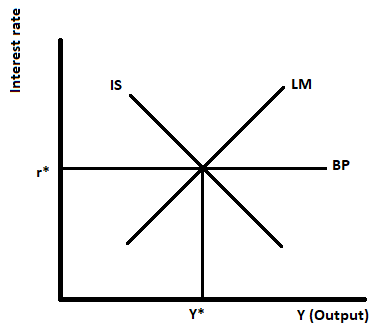
According to the above figure, the x-axis measures the output and the y-axis measures the interest rate. Initially, the economy is in equilibrium and the interest rate is equal to r* which is also the global interest rate. If the domestic and global interest rate is the same then there will be no capital mobility.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









