b) Let X₁, X2, X3,..., X30 be a random sample of size 30 from the population X with the moment generating function given by Suppose that Y = Σ1 Xi, Mx (t) = e(e¹-1) i) Determine the probability density function of Y and find P(6 < Y < 10). ii) Use the central limit theorem to compute P(6
Q: n Show that for any &> 0 and S₁ = 1X₁, lim P(|S₁ - 01 ≥ ) = 0. Show that a statistic S, in a) is the…
A: We will use Chebychev's inequality to calculate the required limit of probability. To obtain the MLE…
Q: Suppose that a pdf for a continuous random variable Y takes the form 1 e-V-u)lo f(y) = y E R where μ…
A: random variable y with given pdf f(y) : y belong to real number (R) then to find probability…
Q: Let X₁, X2, X3.....X be a random sample of n from population X distributed with the following…
A:
Q: A probability mass function for a particular random variable Yhaving nonnegative integer values is…
A:
Q: b) Consider a random variable K with parameter p, whose probability mass function (PM given by f(k)…
A:
Q: b) The probability density function (p.d.f) of the random variable X is given by i) ii) 0≤x≤1 f(x) =…
A:
Q: i) Derive the standard error of ß, se(B) = 0.0009, using MLE approach. ii) Find an approximate 95%…
A: Firstly we have to find the MLE of the parameter and then variance to get the required confidence…
Q: II. The male division Male Data in inches 68 65.5 68.1 65.3 72.5 65.5 65.4 72 71.2 73.2 67.7 73.5…
A: Given that, n=32. The formula for mean and standard deviation is mean=x¯=∑xin standard…
Q: Let X₁, X2, X3, X30 be a random sample of size 30 from a population distributed with the following…
A: Since you have asked multiple question, according to our guidelines we will solve the first question…
Q: a) Let X₁, X₂, ..., Xn denote a random sample from a probability density function given by 1 f(x;…
A: Given X~Gamma(ɑ,1/θ) Note: According to Bartleby guidelines expert solve only one question and…
Q: Let X₁, X2, X3,...,Xn be a random sample of n from population X distributed with the following…
A:
Q: Estimate 6 by the method of moments estimator.
A: In method of moments we equate the sample moments and population moments to get the required…
Q: Let X be a continuous Random variable with probability density function f(x) = 2x , 03/4)
A: Hello! As you have posted more than 3 sub parts, we are answering the first 3 sub-parts. In case…
Q: given by f(k)={pq-1, k=1,2,..... lo, elsewhere i) Derive the moment generating function of K. ii)…
A:
Q: following probability density function: >= { / ² f(x) = e, if 0<x<∞ otherwise Suppose that Y = Σ₁…
A:
Q: Suppose that a sequence of mutually independent and identically distributed discrete random…
A:
Q: a) b) c) Show that for any >0 and S, X₁. lim P(|S, -612 ) = 0. Show that a statistic S, in a) is the…
A: As per bartleby guidelines we can solve only first three subparts and rest can be reposted
Q: ion of (X, Y) is larger than the area below the distri at, random variable 5) of (X, Y), for any…
A:
Q: () () :) What is the parameter space of 8? Find the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) of 0. What is…
A: It is given that the probability density function is f( x; θ ) = { ( θ + 1 )•xθ, 0 < x < 1…
Q: b) Let Y, Y, .,Y, be a random sample from a population with probability density function in part a).…
A:
Q: Let X1,..., Xn be a random sample from a population with probability density function (pdf) f(x | 0)…
A: We have given that Let X 1 ,...,X n be a random sample from a population with probability density…
Q: 1) Let X₁, X2, X3, ... Xn be a sequence of independent and identically distributed with the…
A: As per our guidelines I can solve only first 3 subparts. Kindly post the remaining subpart again and…
Q: P(Z <=)=0.5 Using standard normal table, the value of z corresponding to probability 0.95 is 1.96.
A:
Q: show that 0 is an unbiased
A:
Q: Suppose that {Xn, n 2 1} is a sequence of discrete random variables with distribution function 2i…
A: Hello there! As per the honor code, we are allowed to answer three sub parts at a time, so we are…
Q: Let the function P {(1, 2)} = P {(1, 3)} = P {(2,2)} = P {(2,3)} = 1/6, P {(3, 3) } = 2/6.…
A: a) The associated bivariate distribution function X=1 X=2 X=3 P(Y=y) Y=2 1/6 1/6 0 2/6…
Q: (a) Find a sufficient statistic for 0. (b) Find the maximum likelihood estimator of 0. (c) Find a…
A:
Q: Suppose that a sequence of mutually independent and identically distributed discrete random…
A:
Q: Let Y₁, ₂,.. density function Yn denote a random sample from a uniform distribution with " For…
A: The problem presents a scenario where we have a random sample from a uniform distribution over the…
Q: Give the z-scores for the teacher that are 30 years old and 63 years old (round to two decimal…
A: Introduction: For a random variable, X with mean μ, and standard deviation σ, the z-score is given…
Q: Suppose that a sequence of mutually independent and identically distributed discrete random…
A: Solution: From the given information,
Q: b) Let X₁, X₂, X3.....X be a random sample of n from population X distributed with the following…
A: Given the distribution function of Xi , i = 1 ,2,....n where Xi follows Normal distribution with…
Q: ) Show that = ₁₁X₁ is the maximum likelihood estimator of the parameter 0. Zi=1
A:
Q: i) Use an appropriate method to show that W = is a pivotal quantity. ii) Construct a 90% upper…
A: A quantity is said to be pivotal quantity if it's distribution is free from parameter of interest.

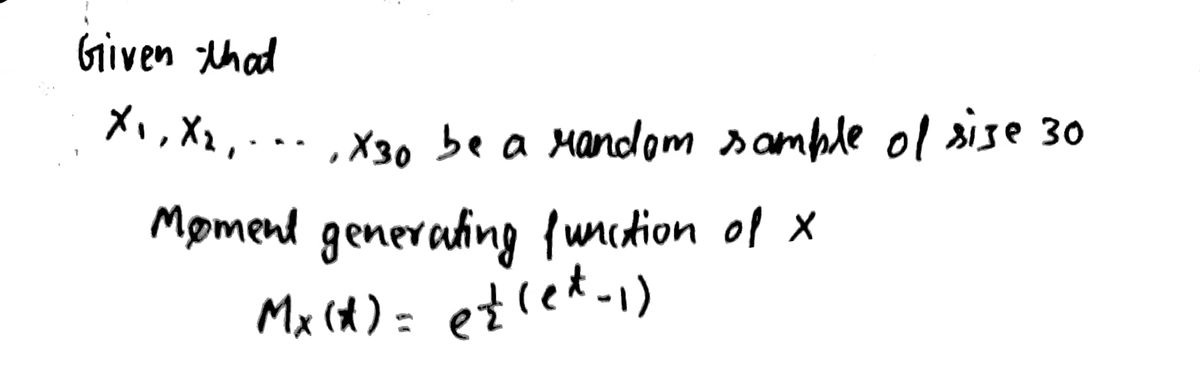
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

- 2)Let X1, X2, ..., Xn be a sample of n units from a population with a probability density function f (x I θ)=θxθ-1 , 0<x<1, θ>0 . According to this: Find the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) of parameter θ.3. Let X, Y be continuous random variables with joint pdf f(x, y). Calculate the joint cumulative distribution function of (X, Y) for each of the pdfs below. (a) f(x, y) = 6e-3x-2y, x, y ≥ 0. (b) f(x, y) = x + ³y²,0 ≤ x, y ≤ 1.Find the moment-generating function for a random variable W with density w-1 e 1< w < 2, f(w) e 0, else.
- Suppose that a sequence of mutually independent and identically distributed discrete random variables X₁, X₂, X3,..., X, has the following probability density function (0%e-0 f(x; 0) = x! 0, I for x = 0,1,2,... elsewhere Show that for any &> 0 and Sn = 1X₁, lim P(|S₁ - 0 ≥ ) = 0. 71-00 Show that a statistic S,, in a) is the maximum likelihood estimator of the parameter 8. Let 0₁ = X₁+2X2+2X₁-X4 and ₂ = (X₁ + X2 + X3 + X4) be two unbiased estimators of 0. Which one of the two estimators is more efficient? ) What is the Cramer-Rao lower bound for the variance of the unbiased estimator of the parameter 0? Use the one-parameter regular exponential family definition to find the functions, h(x), c(0), w(0) and t(x).Let X₁, X2, X3,..., Xn denote a random sample of size n from the population distributed with the following probability density function: e) g) of Ô, Suppose that Ô is a uniform minimum variance unbiased estimator of 0. Show that the variance (0+1)² Var (ê) = ! f(x; 0) = {(0 + 1)xº, 0, n if 0 < x < 1 elsewhere Use part d) of question 2 to show that is a consistent estimator of 0. Show that ₁ ln(X;) is a sufficient estimator of 0. [Hint: Use one-parameter regular exponential family]. Estimate using the method of moment estimator.a) Show for the constant c=g, the function f(x) = c(x+x²) for 0 < x < 1 is a proper density of a probability distribution on (0, 1). b) Find the corresponding cumulative distribution function F(x). c) Find the expected value and standard deviation of the random variable X with density
- Let X₁, X₂, X3,...,Xn be a random sample of n from population X distributed with the fol probability density function: 1 ze=20, f(x;0)=√√2n0 0, if -∞0b) Let X₁, X2, X3.....Xn be a random sample of n from population X distributed with the following probability density function: ze zo, f(x;0)=√2m0 0, (i) Find the parameter space of 0. (ii) Find the maximum likelihood estimator of 0. if -∞b) Let X to be a random sample from a distribution with a probability density function given by f(x; 0) = {0x0-¹,if 0 i) Find the level of significance of the test, a. ii) Calculate the power of the test.b) Let X₁, X2, X3,...,Xn be a random sample of n from population X distributed with the following probability density function: f(x; 0) = 1 -20₁ V2πθ e 0, if - ∞0 < x < 0 otherwise (i) Find the parameter space of 0. (ii) Find the maximum likelihood estimator of 0. (iii) Check whether or not the estimator obtained in (ii) is unbiased. (iv) Find the Fisher information in this sample of size n about the parameter 0.Let Z₁ = X₁-μx ~N(0,1), and Wi σχ = Yi-HY~N(0,1), for i = 1,2,3,...,10, then: oy i) State, with parameter(s), the probability distribution of the statistic, T = ii) Find the mean and variance of the statistic T = Σt, wi? Σ, Z² Σt=1Zi 4i=1 iii) Calculate the probability that a statistic T = Z₁ + W₁ is at most 4. iv) Find the value of such that P(T > B) = 0.01, where T = Σ₁₁Z₁² + 10₁ W₁². ẞ Σ{1Z2 Σi,Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman