Chapter7: Systems Of Equations And Inequalities
Section7.7: Solving Systems With Inverses
Problem 4SE: Can a matrix with an entire column of zeros have an inverse? Explain why or why not.
Related questions
Concept explainers
Transformation of Graphs
The word ‘transformation’ means modification. Transformation of the graph of a function is a process by which we modify or change the original graph and make a new graph.
Exponential Functions
The exponential function is a type of mathematical function which is used in real-world contexts. It helps to find out the exponential decay model or exponential growth model, in mathematical models. In this topic, we will understand descriptive rules, concepts, structures, graphs, interpreter series, work formulas, and examples of functions involving exponents.
Question
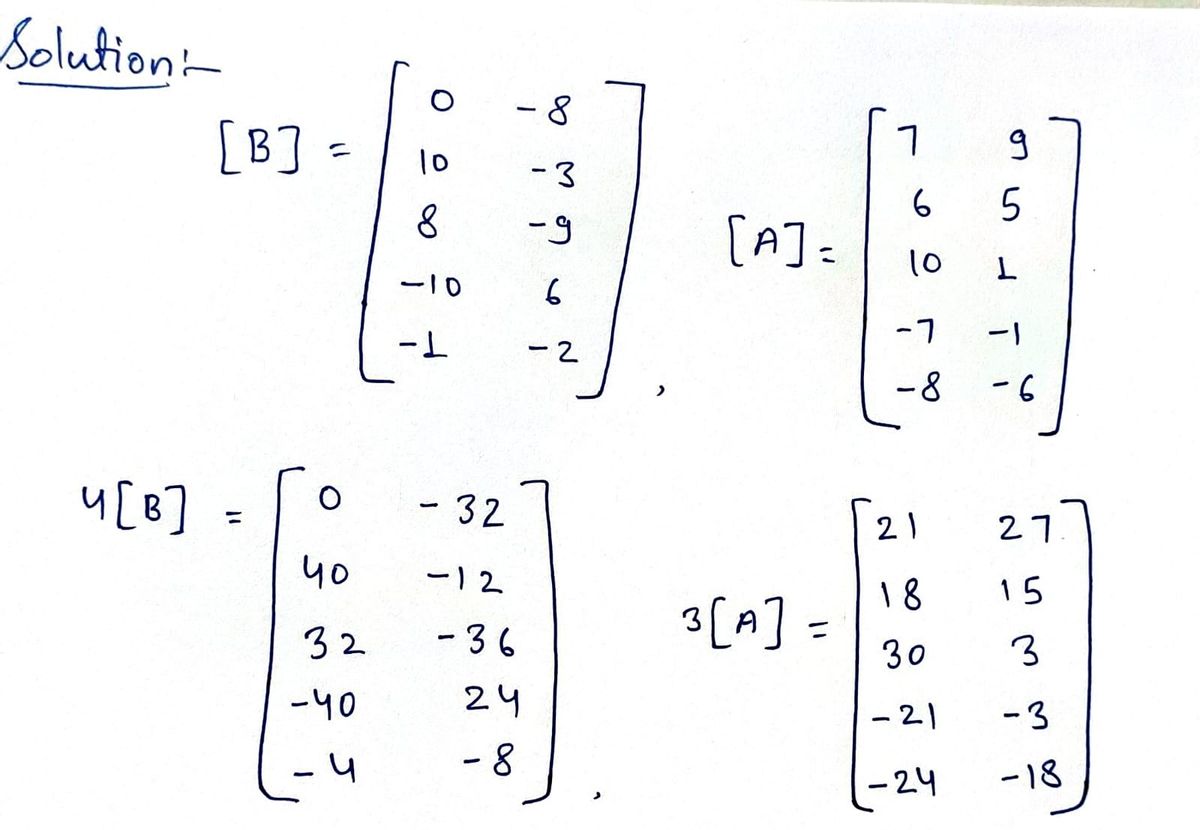
![The image contains two matrices, [B] and [A], along with an expression for a matrix operation.
Matrix [B] is a 5x2 matrix:
\[
[B] = \begin{bmatrix}
0 & -8 \\
10 & -3 \\
8 & -9 \\
-10 & 6 \\
-1 & -2 \\
\end{bmatrix}
\]
Matrix [A] is also a 5x2 matrix:
\[
[A] = \begin{bmatrix}
7 & 9 \\
6 & 5 \\
10 & 1 \\
-7 & -1 \\
-8 & -6 \\
\end{bmatrix}
\]
The expression provided is for calculating \( 4[B] + 3[A] \). There is a blank 5x2 matrix template shown for the result.
To solve \( 4[B] + 3[A] \), multiply each entry of matrix [B] by 4 and each entry of matrix [A] by 3, then add the resulting matrices together.
The steps to compute one element \( (i, j) \) of the resulting matrix are:
\[ (4 \times B_{ij}) + (3 \times A_{ij}) \]
For example, the first element is calculated as:
\[ (4 \times 0) + (3 \times 7) = 0 + 21 = 21\]
Continue this process for each element to fill the blank matrix.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F723d4455-88a3-4468-800e-ec0ca31b017d%2Fd6e82767-fad1-42b4-8867-88b92008a980%2Fjkivn5a_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:The image contains two matrices, [B] and [A], along with an expression for a matrix operation.
Matrix [B] is a 5x2 matrix:
\[
[B] = \begin{bmatrix}
0 & -8 \\
10 & -3 \\
8 & -9 \\
-10 & 6 \\
-1 & -2 \\
\end{bmatrix}
\]
Matrix [A] is also a 5x2 matrix:
\[
[A] = \begin{bmatrix}
7 & 9 \\
6 & 5 \\
10 & 1 \\
-7 & -1 \\
-8 & -6 \\
\end{bmatrix}
\]
The expression provided is for calculating \( 4[B] + 3[A] \). There is a blank 5x2 matrix template shown for the result.
To solve \( 4[B] + 3[A] \), multiply each entry of matrix [B] by 4 and each entry of matrix [A] by 3, then add the resulting matrices together.
The steps to compute one element \( (i, j) \) of the resulting matrix are:
\[ (4 \times B_{ij}) + (3 \times A_{ij}) \]
For example, the first element is calculated as:
\[ (4 \times 0) + (3 \times 7) = 0 + 21 = 21\]
Continue this process for each element to fill the blank matrix.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning