Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:### Table: Coordinate Indices for Atoms
This table provides information on the coordinate indices for atoms in a molecular structure. The table is structured into two main columns: "Atom number" and "Coordinate indices," which further breaks down into x, y, and z coordinates.
#### Columns Description:
- **Atom number**: This column lists the specific number associated with each atom in the molecular structure.
- **Coordinate indices**: This section contains sub-columns for x, y, and z, representing the three-dimensional positioning of each atom respectively.
#### Data Entries:
- **Atom number 5**:
- Includes input fields (denoted by an 'i' icon) for the x, y, and z coordinates.
- **Atom number 7**:
- Includes input fields (denoted by an 'i' icon) for the x, y, and z coordinates.
- **Atom number 12**:
- Includes input fields (denoted by an 'i' icon) for the x, y, and z coordinates.
Each cell under the coordinate indices is designed to input or display the corresponding values for the x, y, and z positions, which are crucial for understanding the spatial configuration of these atoms within a molecular model. The presence of the 'i' icon indicates that further information or interaction (such as entering data) may be available in these fields.

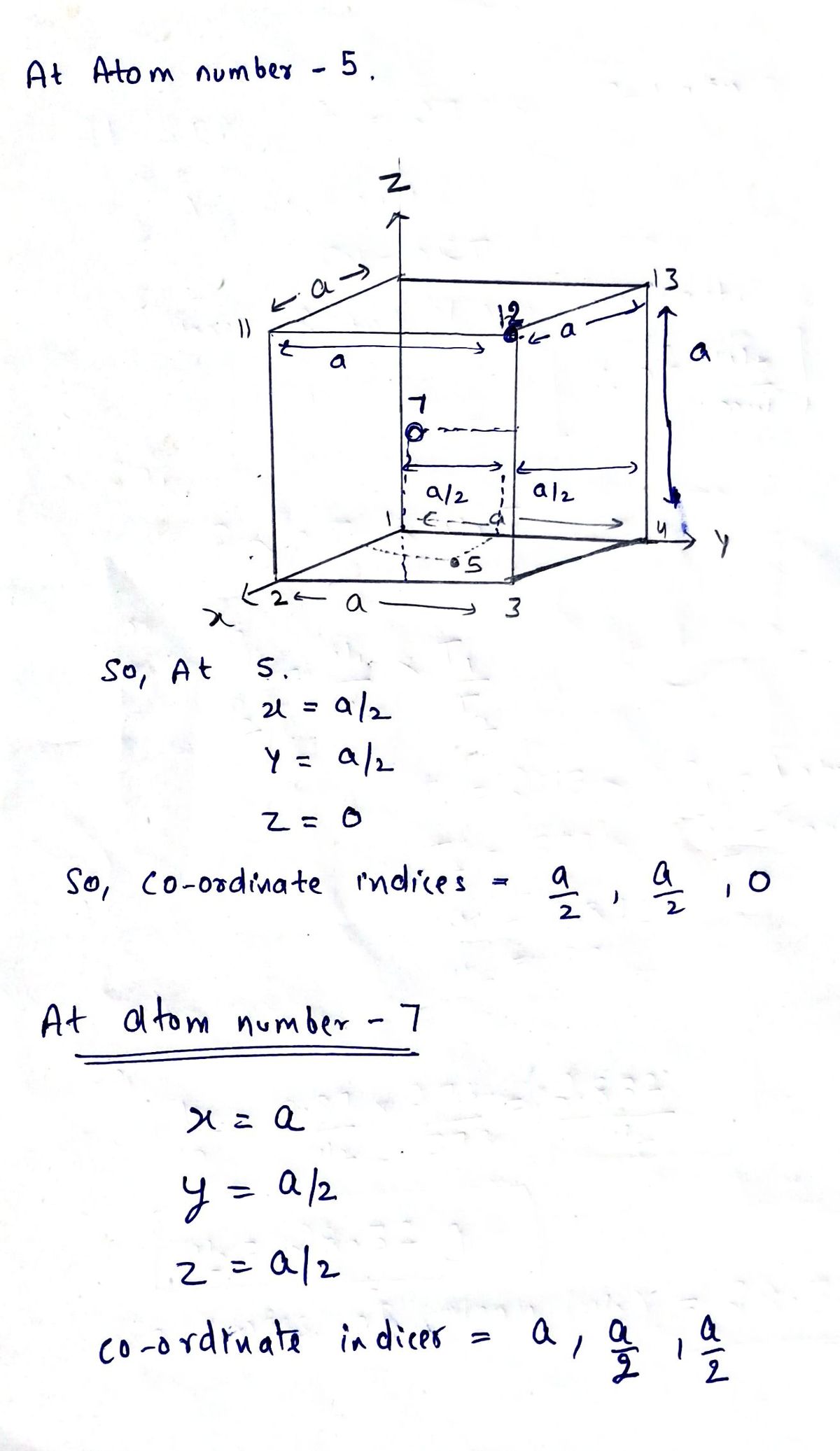
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a three-dimensional cubic lattice structure, commonly used to illustrate atomic arrangements in crystallography.
### Detailed Explanation:
- **Axes**: The structure is oriented along the x, y, and z axes, which represent the three-dimensional space.
- **Lattice Points**: There are 14 labeled lattice points (numbered 1 to 14) represented by red spheres, which indicate the positions of atoms or ions in the structure.
- **Cubic Geometry**:
- The cube is defined by points 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, and 14.
- Each edge of the cube is marked with a length 'a', indicating that the lattice is a cube with equal sides.
- **Planes and Directions**:
- The cube is sectioned into different planar views delineated by lines connecting the lattice points.
- Dotted lines within the cube connect points such as 6 to 12 and 9 to 8, showing the internal structure.
- **Additional Notation**:
- The horizontal distance between lattice points 10 and 13, and the vertical distance between 2 and 11, are both marked as 'a', reinforcing the cubic symmetry.
This structure serves as a fundamental model for understanding unit cells, which are the basic repeating entities in crystalline materials.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY