At the horse races (with ten horses competing), in how many ways can the top three places be selected? (Note that no horse may have more than one of the top three places!)
Permutations and Combinations
If there are 5 dishes, they can be relished in any order at a time. In permutation, it should be in a particular order. In combination, the order does not matter. Take 3 letters a, b, and c. The possible ways of pairing any two letters are ab, bc, ac, ba, cb and ca. It is in a particular order. So, this can be called the permutation of a, b, and c. But if the order does not matter then ab is the same as ba. Similarly, bc is the same as cb and ac is the same as ca. Here the list has ab, bc, and ac alone. This can be called the combination of a, b, and c.
Counting Theory
The fundamental counting principle is a rule that is used to count the total number of possible outcomes in a given situation.
![## Permutations
The fundamental counting principle is applied when the number of options goes down at each station. We will not use or test the formulas here, although it is in the book.
### Example and Exercise:
**Scenario:** In a club of 12 people, in how many ways can a president, vice-president, and treasurer be selected if no person may have more than one office?
The number of ways can be calculated as:
\[ 12 \times 11 \times 10 = 1,320 \text{ ways} \]
**Problem:** At the horse races (with ten horses competing), in how many ways can the top three places be selected? (Note that no horse may have more than one of the top three places!)
The number of ways can be calculated by:
\[ P \times VP \times T \]
The permutations formula applied for the top three places in the race can be solved as:
\[ 10 \times 9 \times 8 \]
So, the number of ways the top three places can be selected is:
\[ = \_\_\_\_\_ \times \_\_\_\_\_ \times \_\_\_\_\_ = \]
### Diagram Explanation:
This exercise includes a blanks graph at the end, encouraging students to compute the results themselves using the given scenarios.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F99f55e7e-eb29-480a-948b-da98465a491e%2F3e774318-31e1-4ebd-8a85-3adc34b59a3f%2Fu5ighe6_reoriented.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Permutation:
The number of different arrangements of ‘r’ elements from a set of‘n’ elements is denoted and given by,
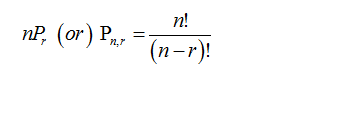
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images




