Analyze the below code. Find the errors in this program and fix them (note: add your comments for explanation). #include //Header files int main() //main function { //declare variables that are used in program float cost1,cost2,cost3; float average; //asking from user to enter three items prices printf("\nEnter three item costs between 1 to 100: ") //entered prices are stored in variables scanf("%f %f %d",cost1,&cost2,&cost3); //formula of average is used. total sum divided by total no average=(cost1+cost2+cost3)/3; if(average>=90) //if condition is true then display following output { printf("Expensive"); } else if(average>=70 & average<90) { //if condition is true then display following output printf("Average"); } else if(average<70); { //if condition is true then display following output printf("Cheap"); } return 0; }
Operations
In mathematics and computer science, an operation is an event that is carried out to satisfy a given task. Basic operations of a computer system are input, processing, output, storage, and control.
Basic Operators
An operator is a symbol that indicates an operation to be performed. We are familiar with operators in mathematics; operators used in computer programming are—in many ways—similar to mathematical operators.
Division Operator
We all learnt about division—and the division operator—in school. You probably know of both these symbols as representing division:
Modulus Operator
Modulus can be represented either as (mod or modulo) in computing operation. Modulus comes under arithmetic operations. Any number or variable which produces absolute value is modulus functionality. Magnitude of any function is totally changed by modulo operator as it changes even negative value to positive.
Operators
In the realm of programming, operators refer to the symbols that perform some function. They are tasked with instructing the compiler on the type of action that needs to be performed on the values passed as operands. Operators can be used in mathematical formulas and equations. In programming languages like Python, C, and Java, a variety of operators are defined.
Analyze the below code. Find the errors in this program and fix them (note: add your comments for explanation).
#include<stdio.h> //Header files
int main() //main function
{
//declare variables that are used in program
float cost1,cost2,cost3;
float average;
//asking from user to enter three items prices
printf("\nEnter three item costs between 1 to 100: ")
//entered prices are stored in variables
scanf("%f %f %d",cost1,&cost2,&cost3);
//formula of average is used. total sum divided by total no
average=(cost1+cost2+cost3)/3;
if(average>=90)
//if condition is true then display following output
{ printf("Expensive"); }
else if(average>=70 & average<90)
{
//if condition is true then display following output
printf("Average");
}
else if(average<70);
{
//if condition is true then display following output
printf("Cheap");
}
return 0;
}
Error : 1 You did not use & operator for the first value.
Error 2: You used %d for the third value. But its a float. so we have to use %f
Code:
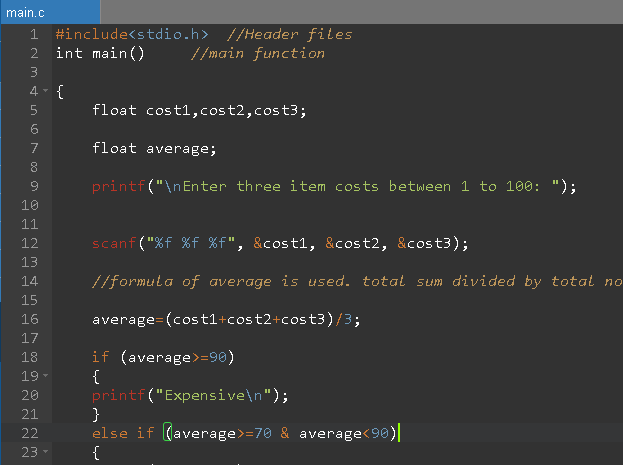
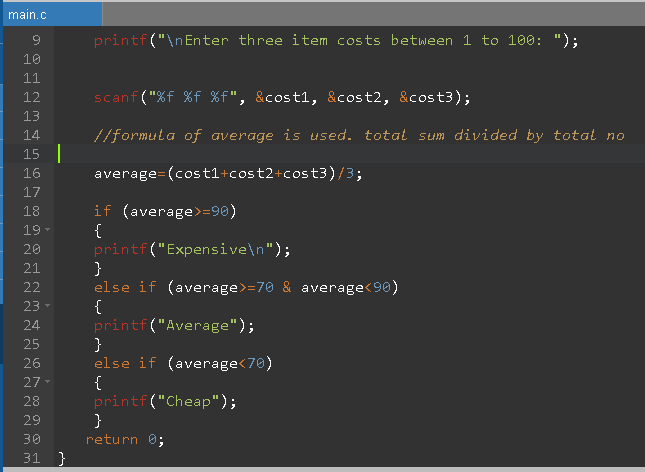
#include<stdio.h> //Header files
int main() //main function
{
float cost1,cost2,cost3;
float average;
printf("\nEnter three item costs between 1 to 100: ");
scanf("%f %f %f", &cost1, &cost2, &cost3);
//formula of average is used. total sum divided by total no
average=(cost1+cost2+cost3)/3;
if (average>=90)
{
printf("Expensive\n");
}
else if (average>=70 & average<90)
{
printf("Average");
}
else if (average<70)
{
printf("Cheap");
}
return 0;
}
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images









