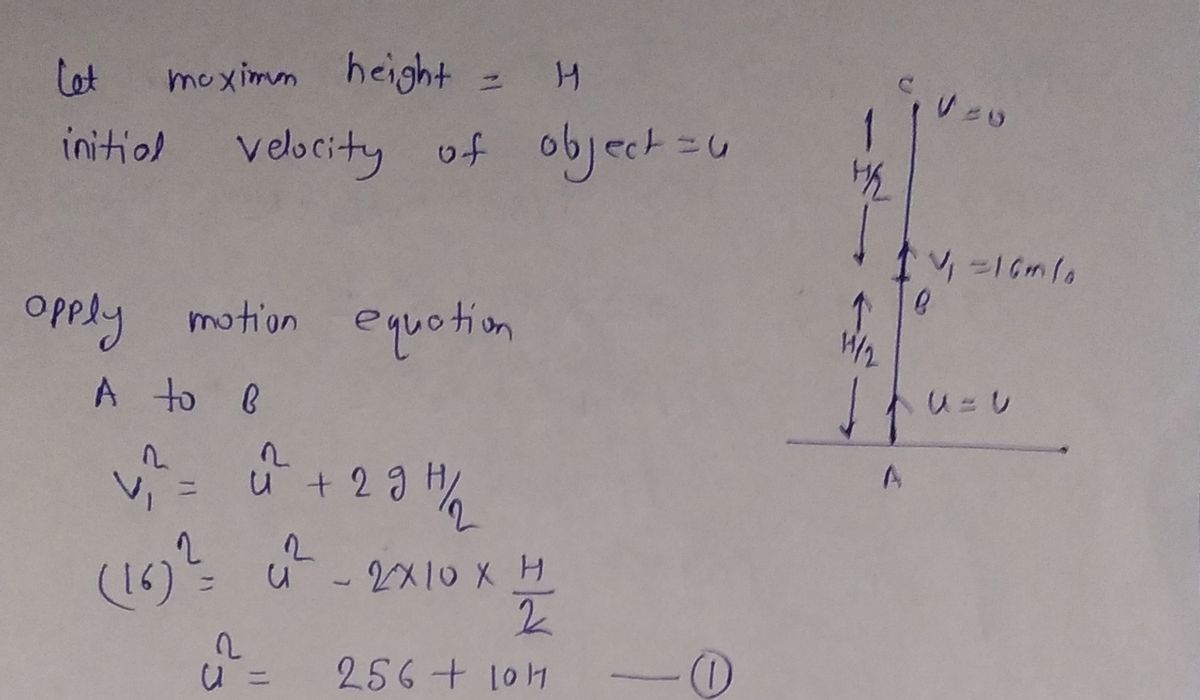
An object is thrown vertically and has an upward velocity of 16 m/s when it reaches 1/2 of its maximum height above its launch point. What is the maximum height of the object?
An object is thrown vertically and has an upward velocity of 16 m/s when it reaches 1/2 of its maximum height above its launch point. What is the maximum height of the object?
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
An object is thrown vertically and has an upward velocity of 16 m/s when it reaches 1/2 of its maximum height above its launch point. What is the maximum height of the object?
---
To solve this problem, we can use the principles of kinematics and energy conservation. Here's a breakdown of the approach:
1. **Identify Known Variables:**
- Initial velocity at half maximum height (v) = 16 m/s
- Gravitational acceleration (g) = 9.8 m/s²
2. **Use the Kinematic Equation:**
- \( v^2 = u^2 + 2as \)
- Here, \( v \) is the velocity at half of the maximum height, \( u \) is the initial velocity, \( a \) is acceleration due to gravity (negative since it's acting downwards), and \( s \) is the distance traveled.
3. **Apply Energy Conservation:**
- At maximum height, the velocity is 0.
- The kinetic energy at half the height is equal to the potential energy gained.
By using these principles, we can calculate the maximum height the object reaches.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON