An immovable charge Q₁ = +5.0μC is placed in fixed location. Another charge, Q₂ = +3.0μC and mass m₂ = 6.0µg, is allowed to move near the first charge. (a) Evaluate the potential energy of Q₂ when it is 4.0 cm from Q₁. (b) If Q₂ starts from rest from a point 4.0 cm from Q₁, what will be its speed when it is 8.0 cm from Q₁? Assume there are no additional forces acting on this charge and Q₁ does not move.
An immovable charge Q₁ = +5.0μC is placed in fixed location. Another charge, Q₂ = +3.0μC and mass m₂ = 6.0µg, is allowed to move near the first charge. (a) Evaluate the potential energy of Q₂ when it is 4.0 cm from Q₁. (b) If Q₂ starts from rest from a point 4.0 cm from Q₁, what will be its speed when it is 8.0 cm from Q₁? Assume there are no additional forces acting on this charge and Q₁ does not move.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:(a) An immovable charge Q₁ = +5.0μC is placed in fixed location. Another charge, Q₂ = +3.0μC
and mass m₂ = 6.0μg, is allowed to move near the first charge. (a) Evaluate the potential
energy of Q₂ when it is 4.0 cm from Q₁. (b) If Q₂ starts from rest from a point 4.0 cm from
Q₁, what will be its speed when it is 8.0 cm from Q₁? Assume there are no additional forces
acting on this charge and Q₁ does not move.
(b) An immovable charge Q₁ = -2.0µC is placed in fixed location at the origin on an (x, y)
coordinate system. Another charge, Q₂ = +1.0μC and mass m₂ = 7.0µg, is allowed to move
near the first charge. (a) Evaluate the potential energy of Q₂ when it is at the location
(3cm, 4cm). (b) If Q₂ starts from rest at the location (3cm, 4cm) what will be its coordinate
location and speed when it is 2.0 cm from Q₁? Assume there are no additional forces acting on
this charge and Q₁ does not move.
Expert Solution
Step 1
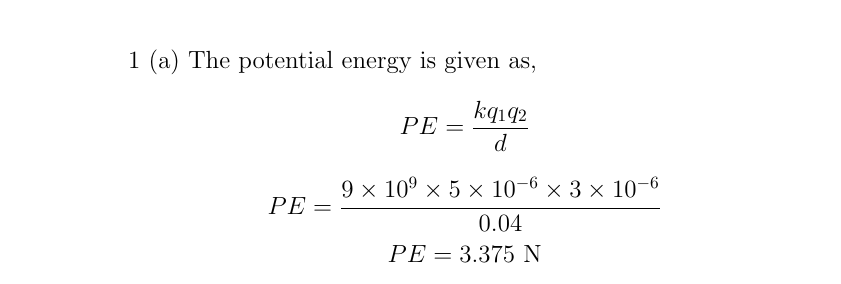
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
