An electric potential exists in a region described by the following: V(x, y, z) = (2.25 -²4) x²y² + (1.503) y²z + 3.00v What is the force that a particle of charge 34 mC feels at position (2.15cm, 2.10cm, -1.25cm)? Give your answer in vector component form. Answer: Force
Q: A point charge Q1 = +4.9 uC is fixed in space, while a point charge Q2 = +2.1 nC, with mass 6.6 ug,…
A: Charge Q1= +4.9 uC = +4.9*10-6CCharge Q2=+2.1 nC = +2.1*10-9 CMass = 6.6 ug = 6.6*10-9 kga) The…
Q: What is the electric potential, in volts, due to the proton on an electron in an orbit with radius…
A:
Q: A rubber sheet of infinite size has an area charge density of σ = -48.5 nC/m^2 spread uniformly on…
A: Given:- The electric field is given by the rubber sheet and glass fiber with line…
Q: A proton's potential energy as a function of distance x from an atomic nucleus, in nm, is given by…
A: At distance of closest approach, the initial kinetic energy of the proton is converted to…
Q: A proton (mass = 1.67 kg, charge = 1.60 x 10-19 C) moves from point A to point B %3D under the…
A: Given data: Mass of the proton mp=1.6×10-27kg Charge, q=1.6×10-19C Speed of the proton at point A…
Q: An electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference ΔV. If the electron reaches a…
A: The objective of the question is to find the potential difference that an electron is accelerated…
Q: The electric potential in a certain region is V = α x^2y^2 + β z^2(x^2 − γ) + δ y^3z , where α = 8…
A: Given: The Electric potential in a certain region V=αx2y2+βz2(x2-γ)+δy3zwhere:α=8 V/m4 , β=4.6 V/m4…
Q: A rubber sheet of infinite size has an area charge density of σ = -66.3 nC/m^2 spread uniformly on…
A: Electric potential difference at a half-way point between the sheet and the glass fiber due to the…
Q: Acart is attached to aspring and made toundergo vibrational motion The position af the cart over…
A: Required : The moments that represent the force diagram.
Q: ositive charge of 20.0µC is placed on a spherical conductor of 10.0cm radius. Find f ectrical field…
A: Given q = 20 ×10-6 C
Q: Cathode ray tubes (CRTS) used in old-style televisions have been replaced by modern LCD and LED…
A: Given: Distance between separated plates (d) = 1.56 cm. Potential difference across the plates (V) =…
Q: PRACTICE: Throughout a particular region of space, the electric potential can be expressed as V =…
A: The electric potential V = 2xz+2y-7z We need to find the electric potential at point P = (7,-8,1)
Q: What is the potential difference between xi = 10 cm and xf = 40 cm in the uniform electric field Ex…
A: Initial position is: Final position is: Electric field is:
Q: Don't use chatgpt, please help.
A:
Q: An electron with charge e and mass m is accelerated from rest through a potential V over a distance…
A:
Q: A point charge q₁ =9.1 μC is held fixed a second point charge q -0.42 µC and a mas: kg is placed on…
A: A point charge is a hypothetical charge located at a single point in space. Here, we calculate the…
Q: Problem 2: Apoint mass of charge q> 0 moves at 35° to a uniform electric field E for a total…
A:
Q: Two widely separated charged metal spheres A and B have the same electrical surface potential. The…
A:
Q: How strong is the electric field in N/C between two parallel plates (5.0000x10^0) mm apart if the…
A:
Q: yed parallel plates are separated by 5.00 mm. A potential difference of 600 V exists between the…
A: d = 5 mmV = 600 volt
Q: In the image provide these exists two parallel plates call A and B the length of both being 5…
A: Since you have posted a question with a multiple sub parts, we will solve first three sub - parts…
Q: A dipole with –Q at the origin (0,0) and the +Q at coordinates x= 4.00 cm, y = 3.00 cm is in an…
A:
Q: In which situation's would angular acceleration be negative? Select all that apply 1. An object is…
A: The rate of change of angular velocity with respect to time is known as angular acceleration. We…

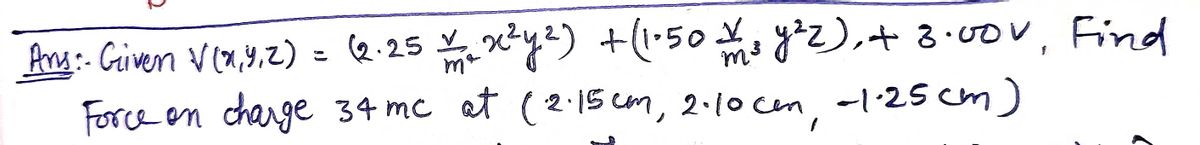
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

- the electric field of 2 plates is E=σ/2ε0 find V (electric potential) by integrating the electric fieldFigure 1 shows two sets of equi-potential surfaces due to charge q₁ and charge 92. An external agent moves an electron (e = 1.6 × 10-¹⁹ C) from position a to position b. 50 V91 25 V 110 V 110 V 92 50 V Figure 1: Two sets of equi-potential surfaces a) State whether the charges q₁ and q2 are positive or negative. Justify your answer.d Q3 Q2 M Q1 n three corners of a square with d=8 cm side length, there are point charges (in red) Q₁=16 pC, Q₂ =-38 pC and Q3 =118 pC. Calculate the difference between the potentials in the middle (V₂) and in the fourth corner (V₁). (V₂-V₁) Write your answer in V with 2 decimals.
- I'm having trouble finding the solution to this problem. This problem is based off the textbook "Physics: Principles with Applications, 7th edition by Douglas C. Giancoli" chapter 16.Four equal negative charges, of magnitude 10C are situated at the corners of a square, with a length of side equal to 3. A small test charge of 0.07C is placed in the exact centre of the square. What is the magnitude of the potential energy of the test charge? Give your answer in GJA proton (mass = 1.67 x 10-27 kg, charge = 1.60 x 10-19 C) moves from %3D point A to point B under the influence of an electrostatic force only. At point A the proton moves with a speed of 50 km/s. At point B the speed of the proton is 87.8 km/s. Determine the potential difference VB-VA (in units of volts). Select one: O A. 20.41 O B. -42.81 OC. -27.18 OD. 2.15 E. 26.66
- = A point charge q₁ 9.1 µC is held fixed at 0.42 μC and a mass origin. A second point charge 2 3.2 x 104 kg is placed on the x-axis, 0.96 m from the origin. The second point charge is released at rest. What is its speed when it is 0.24 m from the origin? =Cathode ray tubes (CRTS) used in old-style televisions have been replaced by modern LCD and LED screens. Part of the CRT included a set of accelerating plates separated by a distance of about 1.38 cm. If the potential difference across the plates was 24.0 kV, find the magnitude of the electric field (in V/m) in the region between the plates. HINT V/mA point charge Q1 = +4.8 μC is fixed in space, while a point charge Q2 = -3.5 nC, with mass 6.4 μg, is free to move around nearby. If Q2 is released from rest at a point 0.44 m from Q1, what will be its speed, in meters per second, when it is 0.25 m from Q1?