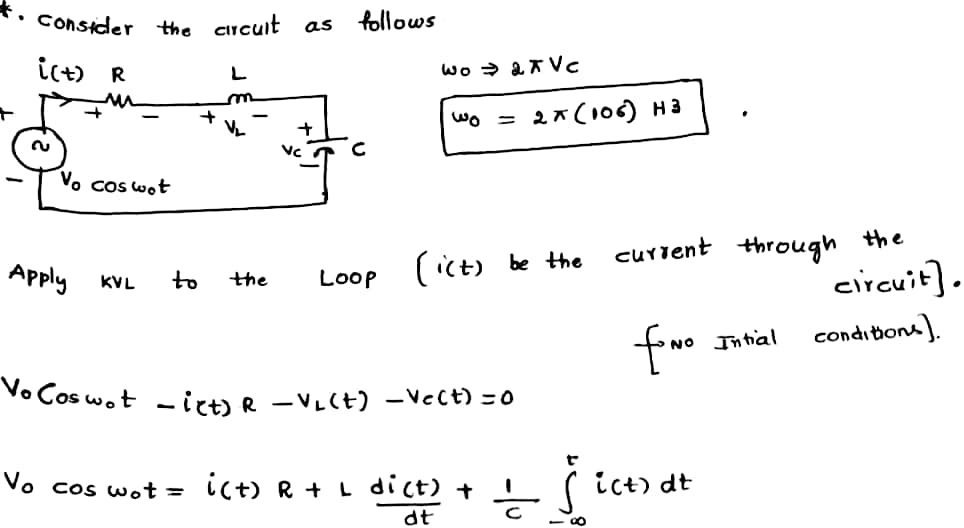
An AM radio station transmits a signal consisting of a carrier wave at frequency vc = 106 Hz. If we can adjust or radio dial just right then this signal will be amplified in comparison to all other signals. A first model of this can be made with an RLC circuit in series. In this case the input is given by the antenna. The incident radio waves create an oscillating voltage in the antenna. We represent this by V0 cos (wo t), where wo = 2π vc and V0 = 1 mV. 1).Given the inductance L = 84.4 μH and resistance R = 5 ohms, solve the differential equation and find the capacitance needed to create a resonance with the incident wave. Think of it this way; as you turn the dial you adjust the gap distance in the capacitor which changes the capacitance in the system and thus changes the natural frequency (fre
An AM radio station transmits a signal consisting of a carrier wave at frequency vc = 106 Hz. If we can adjust or radio dial just right then this signal will be amplified in comparison to all other signals. A first model of this can be made with an RLC circuit in series. In this case the input is given by the antenna. The incident radio waves create an oscillating voltage in the antenna. We represent this by V0 cos (wo t), where wo = 2π vc and V0 = 1 mV.
1).Given the inductance L = 84.4 μH and resistance R = 5 ohms, solve the differential equation and find the capacitance needed to create a resonance with the incident wave. Think of it this way; as you turn the dial you adjust the gap distance in the capacitor which changes the capacitance in the system and thus changes the natural frequency (frequency of the homogeneous solution) of the circuit.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images









