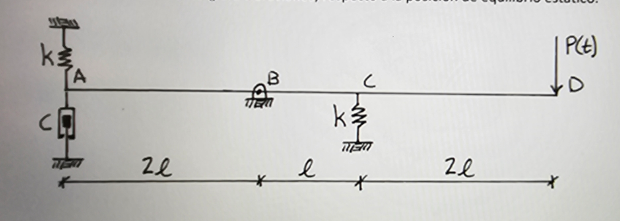
A uniform infinitely rigid beam of mass m and length 5/ is receiving a time-varying force P(t), at its end (point D), as shown in the figure. The beam is supported by a pin at point B, two springs of stiffness k, one at point A and one at point C, and a linear viscous damper with constant c at point A. Prepare a discrete analysis model of a degree of freedom, present the free body and kinetic diagrams. Clearly indicate the degree of freedom and its direction on the diagrams. Use as the mass moment of inertia, Io, of the beam with respect to its centerDetermine the equation of motion (for vibrations) with respect to the static equilibrium position
A uniform infinitely rigid beam of mass m and length 5/ is receiving a time-varying force P(t), at its end (point D), as shown in the figure. The beam is supported by a pin at point B, two springs of stiffness k, one at point A and one at point C, and a linear viscous damper with constant c at point A. Prepare a discrete analysis model of a degree of freedom, present the free body and kinetic diagrams. Clearly indicate the degree of freedom and its direction on the diagrams. Use as the mass moment of inertia, Io, of the beam with respect to its centerDetermine the equation of motion (for vibrations) with respect to the static equilibrium position
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
A uniform infinitely rigid beam of mass m and length 5/ is receiving a time-varying force P(t), at its end (point D), as shown in the figure. The beam is supported by a pin at point B, two springs of stiffness k, one at point A and one at point C, and a linear viscous damper with constant c at point A. Prepare a discrete analysis model of a degree of freedom, present the free body and kinetic diagrams. Clearly indicate the degree of freedom and its direction on the diagrams. Use as the mass moment of inertia, Io, of the beam with respect to its centerDetermine the equation of motion (for vibrations) with respect to the static equilibrium position

Transcribed Image Text:Una viga infinitamente rigida uniforme de masa m y de longitud 51 está recibiendo una fuerza variable en el tiempo
P(t), en su extremo (punto D), como se muestra en la figura. La viga está apoyada por un pasador en el punto B,
dos resortes de rigidez k uno en el punto A y otro en el punto C, y un amortiguador viscoso lineal con constante c
en el punto A. Prepare un modelo de análisis discreto de un grado de libertad, presente los diagramas de cuerpo
libre y cinético. Indique claramente el grado de libertad y su dirección en los diagramas. Utilice como momento
de inercia de masa, lo, de la viga respecto a su centro:
m. (51)²
IG =
12
Determine la ecuación de movimiento (para vibraciones) respecto a la posición de equilibrio estático.
TEM
k
Search
2 l
е
C
k 3
MEM
*
2l
28
P(t)
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given
The moment of inertia of of beam about its center is .
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 7 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY