A train weighing 890 kN is being pulled up a 1.5% slope by a certain force. The train’s resistance is 5 N per kN of its weight, determine the value of this force if the speed of the train is increased from 24kph to 48kph in a span of 450m distance. Solve by: (a) D’ Alembert’s Principle (b) Work-Energy Method
A train weighing 890 kN is being pulled up a 1.5% slope by a certain force. The train’s resistance is 5 N per kN of its weight, determine the value of this force if the speed of the train is increased from 24kph to 48kph in a span of 450m distance. Solve by:
(a) D’ Alembert’s Principle
(b) Work-Energy Method
Provide a clear illustration.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

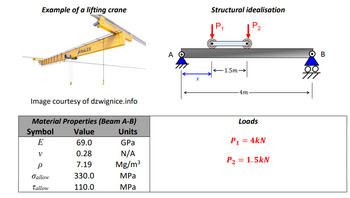
You have been tasked with designing a beam to support a lifting crane. The applied load is offset
from the centre of the carriage used to mount the crane to the overhead beam. Therefore, the loads
applied to the two axels, P1 and P2, differ. The position of the crane can vary (dependent on the
variable, x, shown below).
Example of a lifting crane
Image courtesy of dzwignice.info
Structural idealisation
Material Properties (Beam A-B) Loads
Symbol Value Units
?? = ???
?? = ?. ???
E 69.0 GPa
v 0.28 N/A
ρ 7.19 Mg/m3
σallow 330.0 MPa
τallow 110.0 MPa
Your task is to analyze the structure. To do this you will:
Determine the required section modulus, S, of the beam, based on the material properties
and the maximum bending moment.
Note: the section modulus ? =1/y