A train car has block M₂ on the floor of the car and block M₁ stacked on top of M₂. You acceleration constraints are that M2 and M₁ remain stationary relative to each other and remain on the same part of the train's floor. µs1 = 0.5 refers to the surface between M₁ and M₂ while us2 = 0.25 refers to the surface between M₂ and the floor. a) 5) c) Draw an Interaction Diagram then Free Body Diagrams for each ob- ject in your system that satisfy the con- straints (size of vectors matter). What is the maximum accel- eration the train can have to fulfill the constraints? What is the Force of friction 10kg and M₂ = acting on M₁ if M₁ 30kg? = M₁ M₂ Usi=1/ Hs2=1/
A train car has block M₂ on the floor of the car and block M₁ stacked on top of M₂. You acceleration constraints are that M2 and M₁ remain stationary relative to each other and remain on the same part of the train's floor. µs1 = 0.5 refers to the surface between M₁ and M₂ while us2 = 0.25 refers to the surface between M₂ and the floor. a) 5) c) Draw an Interaction Diagram then Free Body Diagrams for each ob- ject in your system that satisfy the con- straints (size of vectors matter). What is the maximum accel- eration the train can have to fulfill the constraints? What is the Force of friction 10kg and M₂ = acting on M₁ if M₁ 30kg? = M₁ M₂ Usi=1/ Hs2=1/
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:### Problem 3:
**Scenario Description:**
A train car has block \( M_2 \) on the floor of the car and block \( M_1 \) stacked on top of \( M_2 \). The acceleration constraints specify that \( M_2 \) and \( M_1 \) must remain stationary relative to each other and on the same part of the train’s floor. The coefficient of friction \( \mu_{S1} = 0.5 \) refers to the interface between \( M_1 \) and \( M_2 \), while \( \mu_{S2} = 0.25 \) pertains to the interface between \( M_2 \) and the floor.
**Tasks:**
a) **Draw an Interaction Diagram and Free Body Diagrams:**
Create an interaction diagram followed by free body diagrams for each object in the system that comply with the constraints. The sizes of the vectors are significant.
b) **Maximum Acceleration Calculation:**
Determine the maximum acceleration the train can achieve while maintaining the constraints.
c) **Force of Friction Calculation:**
Compute the force of friction acting on \( M_1 \) where \( M_1 = 10 \, \text{kg} \) and \( M_2 = 30 \, \text{kg} \).
**Illustration Description:**
The image depicts a train car with a stick figure standing beside it. Inside the car:
- Block \( M_1 \) is stacked on block \( M_2 \).
- \( \mu_{S1} = 1/2 \) indicates the frictional surface between \( M_1 \) and \( M_2 \).
- \( \mu_{S2} = 1/4 \) indicates the frictional surface between \( M_2 \) and the floor of the train car.
Expert Solution
Step 1
(a) The free body diagram is
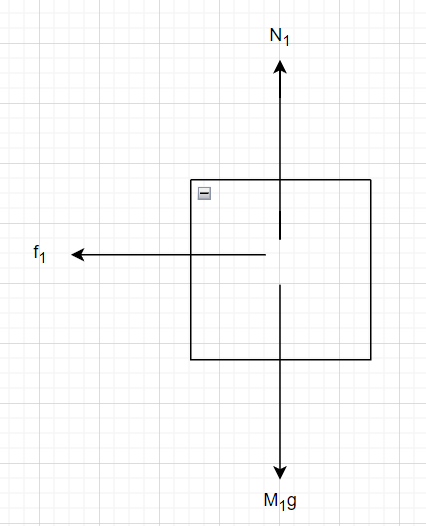
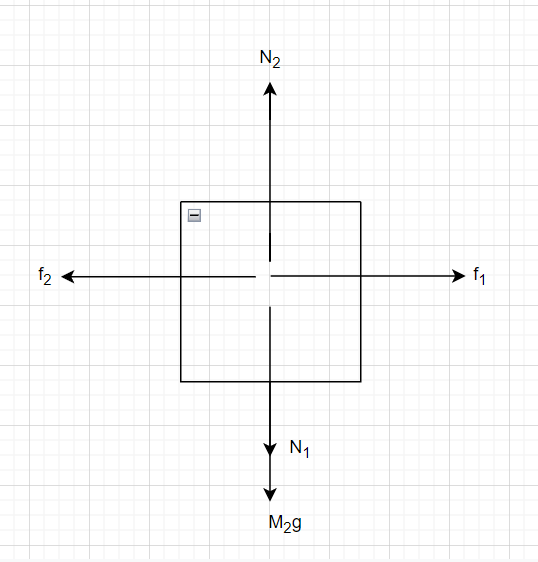
(b) For mass
Equate the forces along vertical direction
The frictional force is
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
