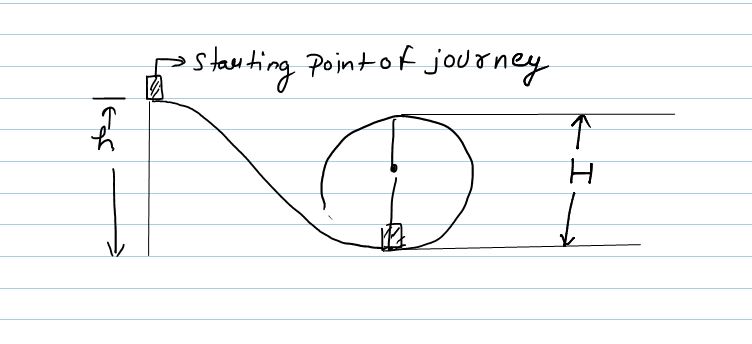
A stuntman rides a sleigh from rest, down a hill to ground level, to a complete vertical loop, and emerges on the other end of the loop at ground level. If the height of the loop is H, how high does the stuntman have to start to ensure that he can completethe loop safely? Assume the sleigh’s motion is frictionless
Q: A block weighing 2.50 kg begins its motion from a stationary position at point A, located at the…
A:
Q: box with mass m goes down a ramp that makes an angle of 60 º with the horizontal. The ramp bands…
A:
Q: A hand pushes a 10 kg block along a table from point A to point C as shown in the figure below. The…
A:
Q: While a roofer is working on a roof that slants at 41.0° above the horizontal, he accidentally…
A: Given:Angle of slant of the roof: θ=41°The weight of the object: Fw=91 NThe Kinetic friction force:…
Q: 8. A block with a mass of 30 kg, starting from rest, slides from the top of an inclined plane. The…
A:
Q: A block weighing 2.50 kg begins its motion from a stationary position at point A, located at the…
A: Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a…
Q: The 40 kg crate is traveling to the right with an initial v0=1.2 m/s, when a person begins to pull…
A: Given, mass of block = 40 kg initial velocity = 1.2 m/s
Q: Two parallel plates 12 cm on a side are given equal and opposite charges of magnitude 5.4×10-9 C.…
A:
Q: In the figure, a 3.7 kg block slides along a track from one level to a higher level after passing…
A:
Q: along the horizontal at its end, which is 0.610 m above the ground. When she leaves the track, she…
A:
Q: A 2.10 kg block is pulled up force on the block from th- Number i
A:
Q: A toboggan starts from rest on parliament hill which is 5.0 m above road level. The toboggan slides…
A:
Q: 3. In the figure, a block slides along a track from one level to a higher level after passing…
A: To determine: A block is sliding along a track from one level to the higher level passing through an…
Q: A heavy rock and a light rock are dropped from the same height and experience no significant air…
A:
Q: Two identical sleds slide down two frictionless hills, each starting from rest at the top of its own…
A: The relation between the speeds and distance travelled s is v2-u2 =2as , where v is the final speed…
Q: m h2 h1
A: mass of block (m) = 10 kg Distance along the flat muddy section (d) = 1 m coefficient of kinetic…
Q: A 400. kg cart slides along the track shown in the image, beginning at point A. It starts from rest…
A:
Q: Given the graph of position vs time (picture), draw appropriate graphs of velocity vs time and…
A: The slope of y-t graph gives velocity. The slope of v-t graph gives acceleration.
Q: A box starts to slide from rest down a smooth inclined plane. as illustrated in the figure. The…
A:
Q: A truck travels uphill with constant velocity on a highway with a 8.0° slope. A 35-kg package sits…
A: M= 35 kg S= 295m Angle is 8°
Q: A block weighing 2.50 kg begins its motion from a stationary position at point A, located at the…
A: Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a…
Q: Kinetic energy at C A 2.25 kg block is placed at position A on the 4.10 m track. path CD of the…
A: Given Length of AB SAB = 4.10 m Length of BC SBC = 1.20 m Mass of block m = 2.25 kg coefficient of…
Q: A 3kg block slides along a floor with coefficient of kinetic friction μk=0.3, initially moving at…
A:
Q: b) A block slides up a ramp that has an angle of 42° with respect to the horizontal. At the bottom…
A:
A stuntman rides a sleigh from rest, down a hill to ground level, to a complete vertical loop, and emerges on the other end of the loop at ground level. If the height of the loop is H, how high does the stuntman have to start to ensure that he can completethe loop safely? Assume the sleigh’s motion is frictionless
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

- Question 23 Two frisky otters slide down frictionless hillsides of the same height but different slopes. The slope of the hill of otter 1 is 30°, while the slope of the hill of otter 2 is 60°. If both start from rest, which otter is moving faster when she reaches the bottom of her hill? O The otter that took the shorter time is moving faster. O Otter 2 is moving faster. O The heavier otter is moving faster, no matter which hill she used. O Otter 1 is moving faster. O Both otters have the same speed at the bottom.Computation. A block is released from rest at the top of a 47-m long frictionless ramp inclined at 34° above the horizontal. What is the block's speed at the bottom of the ramp? v= m/s Record your numerical answer below, assuming three significant figures. Remember to include a "-" if/when necessary.A 3.50 kg block is pulled up a frictionless inclined plane by a 60.0 N force that is parallel to the plane, starting from rest.The normal force on the block from the plane has magnitude 15.2 N.What is the block's speed when its displacement up the ramp is 3.40 m? Number i Units
- The ABC part of the road in the figure is frictionless, beyond C the friction coefficient is u = 0.5. A ball with m = 2 kg is thrown from point A with a speed of 3 m / s. How many meters will the ball travel from point C until it stops? 3m/s 1.2 m a) 3.24 m b) O 2.53 m C) O 2.82 m d) 4.14 m e) 1.24 mA 02 UBC Engineering A trapeze artist of a mass of M to 01 trick. If the ropes do NO work on the artist, what is the speed just before they let go? What is their normal acceleration? 79kg is attempting a new trick on a rope of l 70° and then rope A is cut. The artist holds on until when 02 = 15° then lets go for the next 15m. They are lifted Neglect size and air resistanceA block weighing 2.50 kg begins its motion from a stationary position at point A, located at the highest point of a frictionless ramp. The ramp is inclined at an angle of 40° relative to the horizontal and has a length of 1.50 m. As the block slides down the ramp, it reaches a region between point B and point C, which is a rough horizontal surface with a kinetic friction coefficient of 0.30. After covering a distance of 1.00 m on the horizontal surface, the block encounters a lightweight spring with a spring constant of 900 N/m. By employing the work-energy theorem, determine the velocity of the block at point C just before it collides with the spring?
- A 4.00kg block moves with an initial speed of3.50 km/h downhillover an inclined plane as shown in the figure. The height of the inclined plane is 51.3cm and the friction coefficient between the block and the incline is 0.120. a.How much is the speed of the block at the midpoint of the inclined side. b.How much is the speed of the block at the bottom of the inclined side.10. Block 1 with a mass of 1.0 kg slides down a frictionless ramp with a height of 3.0 m and cllides with block 2 which has a mass of 2.0 kg. The flat surface has friction with a friction coefficient of 0.50. 2 a. Determine the speed of block 1 when it reaches the bottom of the ramp.6. Two packages that start sliding down a 20° ramp from rest a distance d = 4.30 m. For package A: Ma = 5.00 kg and ukA = 0.30. %3D For package B: mB = 7.00 kg and ukB = 0.20. Find the speed of both packages when they reach the bottom. 20°
- Asap6. Two blocks are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley as shown in the figure. Block m1, initially at rest, is released from height h above the table. Block m,, which is the heavier block, begins to fall, while block m2 rises. a) Calculate the speed of m2 just as m¡ hits the table. b) Suppose block m, continues to rise without obstruction even after block m, hits the table. Calculate the maximum height above the table to which m2 rises. hpervious question: Same type of track as in the previous problem, this time with d = 4.73 m. The block starts at x = 0, and is given a push to the left with an initial speed of 7.57 m/s, so it starts sliding up the track to the left. At what value of x will the block reverse direction and start sliding back down? New question: OK, same sort of track, but now with d = 2.12 m. Now suppose the blocks starts on the track at x = 4.10 m. The block is given a push to the left and begins to slide up the track, eventually reaching its maximum height at x = 0, at which point it turns around and begins sliding down. What was its initial speed in this case? 18.98 m/s 12.47 m/s 8.82 m/s 14.90 m/s