A student cOllected hydrogen gas over water at 248.5 K 0.9983 atm atmospheric pressure, using 0.075g of magnes.um. The partial pressure of water at that tempature was 0.01537 atm. The vdume of hydrog.en collected was oo725 L. What is the valve of the gas constant,R?

The proportionality constant helpful to derive ideal gas equation using various state functions of any particular gas is known as the gas constant. It is designated using the symbol "R" and has standard units of L.atm/K.mol.
Given:
The mass of magnesium is 0.075 g.
The temperature is 248.5 K.
The volume of hydrogen is 0.0725 L.
The atmospheric pressure is 0.9983 atm.
The partial pressure of water is 0.01537 atm.
The hydrogen gas is formed by Mg as shown below.
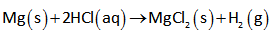
In the above reaction, 1 mole of magnesium react with 2 moles of HCl and produces 1 moles of MgCl2 and 1 moles of H2.
First calculate the moles of hydrogen produced by 0.075 g of Mg.
The formula to calculate moles is shown below.
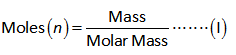
The molar mass of Mg is 24.30 g/mol.
Substitute the values of Mg in equation (I).
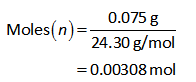

Therefore, 0.00308 moles of Mg will produce 0.00308 moles of hydrogen.
The value of gas constant is calculated by ideal gas equation as shown below.
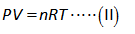
Here,
The pressure of hydrogen gas is “P”.
The volume of hydrogen gas is “V”.
The number of moles of hydrogen gas is “n”.
The gas constant is “R”.
The temperature is “T”.
The pressure of dry hydrogen gas is calculated as shown below.

Substitute all known values in equation (II) to calculate “R”.

Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 8 images









