A steel beam, of lengths a= 6 m and b = 3 m and a hollow box cross section, is supported by a hinge support A and roller support B, see Figure Q.1. The width and height of the cross section are 200 mm and 300 mm, respectively, and the wall thickness of the cross section is 5 mm. The beam is under a distributed load of the intensity that linearly varies from q=0 kN/m to q = 3.1 kN/m for AB span; and is constant with q=3.1 kN/m for BC span. The Young's modulus of steel is 200 GPa. Part A Calculate: A y, v a 5 mm 200 mm Figure Q.1 9 ÅB 300 mm b C 81 X
A steel beam, of lengths a= 6 m and b = 3 m and a hollow box cross section, is supported by a hinge support A and roller support B, see Figure Q.1. The width and height of the cross section are 200 mm and 300 mm, respectively, and the wall thickness of the cross section is 5 mm. The beam is under a distributed load of the intensity that linearly varies from q=0 kN/m to q = 3.1 kN/m for AB span; and is constant with q=3.1 kN/m for BC span. The Young's modulus of steel is 200 GPa. Part A Calculate: A y, v a 5 mm 200 mm Figure Q.1 9 ÅB 300 mm b C 81 X
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
100%
please confirm the answer for this.

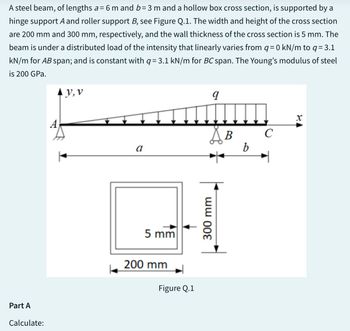
Transcribed Image Text:A steel beam, of lengths a= 6 m and b= 3 m and a hollow box cross section, is supported by a
hinge support A and roller support B, see Figure Q.1. The width and height of the cross section
are 200 mm and 300 mm, respectively, and the wall thickness of the cross section is 5 mm. The
beam is under a distributed load of the intensity that linearly varies from q = 0 kN/m to q = 3.1
kN/m for AB span; and is constant with q= 3.1 kN/m for BC span. The Young's modulus of steel
is 200 GPa.
Part A
Calculate:
A
y, v
a
5 mm
200 mm
Figure Q.1
9
S B
300 mm
b
с
X

Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Calculate:
a) the vertical support reaction in support A. When sketching FBD, set the positive directions of
both reactions in the positive direction of yaxis. Enter your answer in kN to three decimal
places.
Answer:
Check
Question 2
Flag question
b) the vertical support reaction in support B. Enter your answer in kN to two decimal places.
Answer:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
The next sub question

Transcribed Image Text:c) the value of the maximum bending moment in the beam. Enter your answer in kNm to three
decimal places.
Note: when deriving internal moment equations, use the following orientation of x coordinate:
• Segment AB: x changes from 0 at support A to a at support B. After making the cut, keep
the part of the beam left from the cut.
• Segment BC: xchanges from a at support B to L at point C, where L = a + b. After making
the cut, keep the part of the beam right from the cut, i.e. distance from point C to the cut
is equal L-x.
Answer:
Check
d) the maximum normal stress in the cross-section of the beam. Enter the positive value of the
stress. Enter your answer in MPa to two decimal places.
Transcribed Image Text:A steel beam, of lengths a= 6 m and b= 3 m and a hollow box cross section, is supported by a
hinge support A and roller support B, see Figure Q.1. The width and height of the cross section
are 200 mm and 300 mm, respectively, and the wall thickness of the cross section is 5 mm. The
beam is under a distributed load of the intensity that linearly varies from q = 0 kN/m to q = 3.1
kN/m for AB span; and is constant with q= 3.1 kN/m for BC span. The Young's modulus of steel
is 200 GPa.
Part A
Calculate:
A
y, v
a
5 mm
200 mm
Figure Q.1
9
S B
300 mm
b
с
X
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning