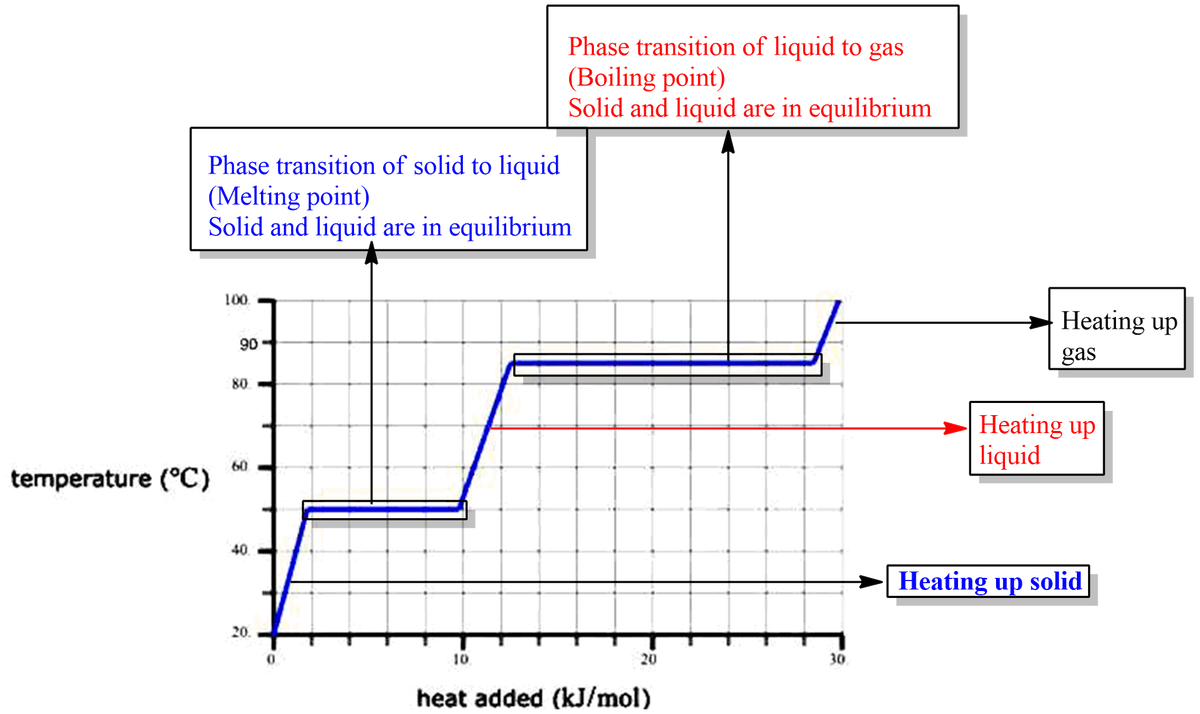
A pure solid sample of Substance X is put into an evacuated flask. The flask is heated at a steady rate and the temperature recorded as time passes. Here is graph of the results: temperature (°C) 100. 80. 60. 40. 20. 0. 10. heat added (kJ/mol) Use this graph to answer the following questions: What is the boiling point of X? What phase (physical state) of X would you expect to find in the flask after 7 kJ/mol of heat has been added? °C 20. (check all that apply) solid liquid gas 30.
States of Matter
The substance that constitutes everything in the universe is known as matter. Matter comprises atoms which in turn are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. Different atoms combine together to give rise to molecules that act as a foundation for all kinds of substances. There are five states of matter based on their energies of attraction, namely solid, liquid, gases, plasma, and BEC (Bose-Einstein condensates).
Chemical Reactions and Equations
When a chemical species is transformed into another chemical species it is said to have undergone a chemical reaction. It consists of breaking existing bonds and forming new bonds by changing the position of electrons. These reactions are best explained using a chemical equation.

Basic description of the graph is shown below-
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images









