A process is being designed to extract 95% ofChloramphenicol from a clarified broth, where the extraction time must be of the order of a few minutes. The solvent is n-amyl acetate and the partition coefficient is 16. Optimal data have been obtained from a small POD having a rotating cylinder of 20-cm diameter and 2.5-cm length, operating at 9,000 rpm with a volumetric feed-to-solvent ratio of 4 and a broth feed rate of 920 mL/minute. A commercial- size POD is available with a rotating cylinder of 91-cm diameter and 91-cm length, operating at a maximum rpm of 2,100. Compute the broth feed rate that could be handled by this commercial POD.
A process is being designed to extract 95% ofChloramphenicol from a clarified broth, where the extraction time must be of the order of a few minutes. The solvent is n-amyl acetate and the partition coefficient is 16. Optimal data have been obtained from a small POD having a rotating cylinder of 20-cm diameter and 2.5-cm length, operating at 9,000 rpm with a volumetric feed-to-solvent ratio of 4 and a broth feed rate of 920 mL/minute. A commercial- size POD is available with a rotating cylinder of 91-cm diameter and 91-cm length, operating at a maximum rpm of 2,100. Compute the broth feed rate that could be handled by this commercial POD.
Feed to solvent ratio is given as 4. Thus,
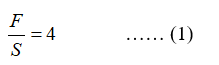
Also, the partition coefficient is given as:
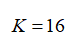
Calculate the extraction factor (E) as:
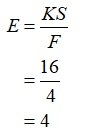
Now, calculate the theoretical number of stages using this extraction factor and fraction of unextracted Chloramphenicol (5%) as:
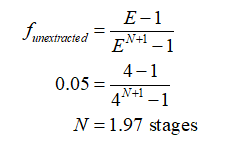
Feed rate is given as, F = 920 mL/min. Solvent rate is calculated as:
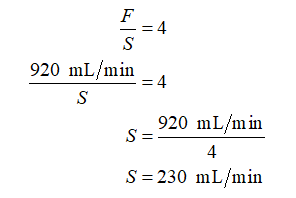
Further, calculate the nominal residence time (tnom) for the small POD as:
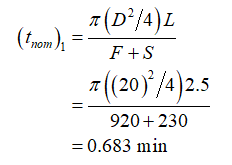
Calculate the value of angular velocity (ω1) and dimensionless acceleration G1 for small POD as:
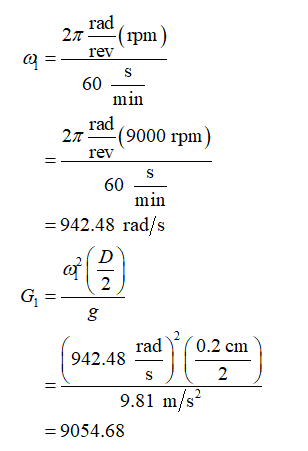
Step by step
Solved in 10 steps with 13 images









