A political campaign is interested in whether city 1 has less support for raising the minimum wage than city 2. Polls were conducted in the two largest cities in the state about raising the minimum wage. In city 1, a poll of 800 randomly selected voters found that 539 supported raising the minimum wage. In city 2, a poll of 1000 randomly selected voters found that 657 supported raising the minimum wage. What type of hypothesis test should be performed? P1 = P2 = Test statistic = p-value = Does sufficient evidence exist to support the claim that the level of support in city 1 is lower than that of city 2 at the a = 0.05 significance level? Select v
A political campaign is interested in whether city 1 has less support for raising the minimum wage than city 2. Polls were conducted in the two largest cities in the state about raising the minimum wage. In city 1, a poll of 800 randomly selected voters found that 539 supported raising the minimum wage. In city 2, a poll of 1000 randomly selected voters found that 657 supported raising the minimum wage. What type of hypothesis test should be performed? P1 = P2 = Test statistic = p-value = Does sufficient evidence exist to support the claim that the level of support in city 1 is lower than that of city 2 at the a = 0.05 significance level? Select v
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
See the attached images and help me with solving

Transcribed Image Text:**Question: What type of hypothesis test should be performed?**
**Options:**
- Right-tailed Z test
- Left-tailed Z test
- Left-tailed T test
- Two-tailed Z test
(Note: The options outlined above refer to different types of statistical hypothesis tests. Each test is appropriate for different scenarios based on the distribution and nature of the data.)
![A political campaign is interested in whether city 1 has less support for raising the minimum wage than city 2. Polls were conducted in the two largest cities in the state about raising the minimum wage. In city 1, a poll of 800 randomly selected voters found that 539 supported raising the minimum wage. In city 2, a poll of 1000 randomly selected voters found that 657 supported raising the minimum wage.
What type of hypothesis test should be performed? [Dropdown menu for selection]
\[
\hat{p}_1 = \text{[input box]}
\]
\[
\hat{p}_2 = \text{[input box]}
\]
\[
\hat{p} = \text{[input box]}
\]
Test statistic = [input box]
\( p \)-value = [input box]
**Question:** Does sufficient evidence exist to support the claim that the level of support in city 1 is lower than that of city 2 at the \( \alpha = 0.05 \) significance level? [Dropdown menu for selection]](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F0bd5c466-4067-47de-aefa-e4955ebdfa80%2F198da73d-aa1a-4ed2-8884-4e0b34bcc8aa%2Fayaasfg_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:A political campaign is interested in whether city 1 has less support for raising the minimum wage than city 2. Polls were conducted in the two largest cities in the state about raising the minimum wage. In city 1, a poll of 800 randomly selected voters found that 539 supported raising the minimum wage. In city 2, a poll of 1000 randomly selected voters found that 657 supported raising the minimum wage.
What type of hypothesis test should be performed? [Dropdown menu for selection]
\[
\hat{p}_1 = \text{[input box]}
\]
\[
\hat{p}_2 = \text{[input box]}
\]
\[
\hat{p} = \text{[input box]}
\]
Test statistic = [input box]
\( p \)-value = [input box]
**Question:** Does sufficient evidence exist to support the claim that the level of support in city 1 is lower than that of city 2 at the \( \alpha = 0.05 \) significance level? [Dropdown menu for selection]
Expert Solution
Step 1
From the provided information,
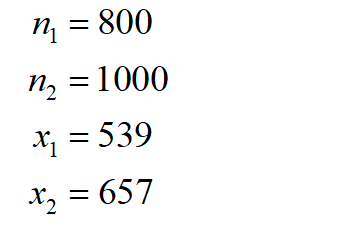
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman