A man is walking through a maze with 6 electric gates independent of each other. Let Ai = be the case that a door works. P(A1) = 0.7 P(A2) = 0.4 P(A3 ) = 0.5 P(A4 ) =0.9 P(A5) = 0.3 P(A6)= 0.6 See picture for path. C = (A5 ∩ A6 ) ∪ A3 Evaluate P(C)
A man is walking through a maze with 6 electric gates independent of each other. Let Ai = be the case that a door works.
P(A1) = 0.7 P(A2) = 0.4 P(A3 ) = 0.5 P(A4 ) =0.9 P(A5) = 0.3 P(A6)= 0.6
See picture for path.
C = (A5 ∩ A6 ) ∪ A3 Evaluate P(C)

Event: In probability theory, an event is an outcome or a set of outcomes of a random experiment to which a probability is assigned. A single outcome is an element of a sample space and different events in a random experiment are generally not equally likely, since they may include very different groups of outcomes.
Union of Two Events: For any two events A and B, union of A and B, written as , is defined as the occurrent of either A or B or both. In other words, it is the occurrent of at least one of A and B.
Intersection of Two Events: For any two events A and B, intersection of A and B, written as , is defined as the occurrent of A and B both.
Independent Events: A number of events are said to be independent if the probability of occurrence of any one of them is not affected by the supplementary information regarding the occurrence of any number of the remaining events.
Let there are n independent events A1, A2, ... , An with P(Ai) > 0 for all i = 1, 2, ... , n. Then we have,
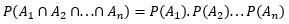
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









