A mail-order computer business has six telephone lines. Let X denote the number of lines in use at a specified time. Suppose the pmf of X is as given in the accompanying table. Calculate the probability of each of the following events. a. {at most three lines are in use} b. {fewer than three lines are in use} c. {at least three lines are in use} d. {between two and five lines, inclusive, are in use} e. {between two and four lines, inclusive, are not in use} f. {at least four lines are not in use}
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
A mail-order computer business has six telephone lines.
Let X denote the number of lines in use at a specified
time. Suppose the pmf of X is as given in the accompanying table.
Calculate the probability of each of the following events.
a. {at most three lines are in use}
b. {fewer than three lines are in use}
c. {at least three lines are in use}
d. {between two and five lines, inclusive, are in use}
e. {between two and four lines, inclusive, are not in use}
f. {at least four lines are not in use}

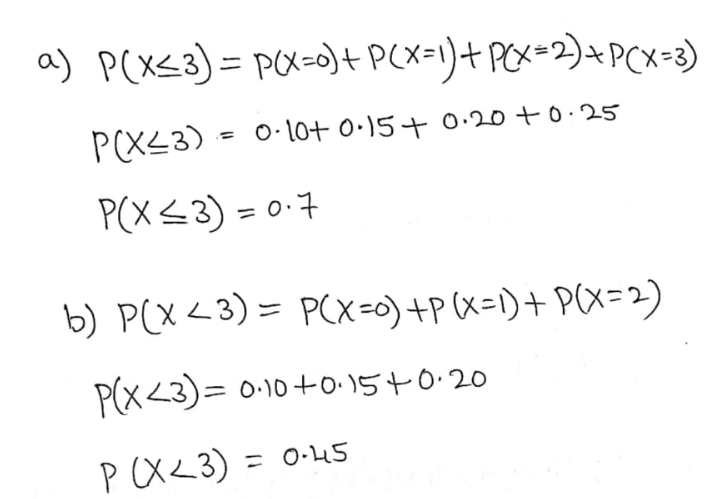
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images









