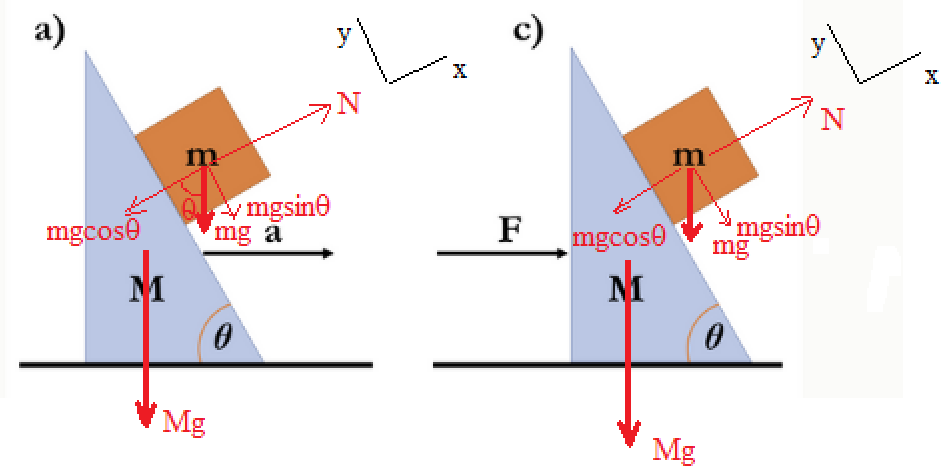
a) M m 0 a û F M m 0 A block of mass m rests on a frictionless wedge which has a mass M and whose surface makes an angle to the horizontal as shown. An external force F is acting on the wedge causing it to move to the right with constant acceleration. a) Find the acceleration to the right such that the block m remains stationary relative to the wedge. Express your answer in terms of m, 0, g, and M, as needed. b) Describe qualitatively the motion of the block if the wedge had a greater acceleration than the one obtained in a). c) What is the magnitude of the force F for which the two objects move with the same acceleration as in part a)? Express your answer in terms of m, 0, g, and M, as needed. In your solution, clearly indicate the coordinate axes you will use to write the forces. Include all the relevant free body diagrams and label the forces with double subscript notation.
a) M m 0 a û F M m 0 A block of mass m rests on a frictionless wedge which has a mass M and whose surface makes an angle to the horizontal as shown. An external force F is acting on the wedge causing it to move to the right with constant acceleration. a) Find the acceleration to the right such that the block m remains stationary relative to the wedge. Express your answer in terms of m, 0, g, and M, as needed. b) Describe qualitatively the motion of the block if the wedge had a greater acceleration than the one obtained in a). c) What is the magnitude of the force F for which the two objects move with the same acceleration as in part a)? Express your answer in terms of m, 0, g, and M, as needed. In your solution, clearly indicate the coordinate axes you will use to write the forces. Include all the relevant free body diagrams and label the forces with double subscript notation.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Pushing a Block and a Wedge
0 points possible (ungraded)
In the following problem, you are asked to:
i) Define the system and the environment:
Identify which objects - the environment - interact with the object of interest - the system. Justify your choice of system: would
a different choice also work? If not, why not? If so, why is the choice you made better?
ii) Describe the interactions and the resulting forces:
Identify the forces exerted on the object of interest by the other objects.
iii) Draw the free body diagram of the object:
Make sure that each force arrow is labeled with two subscripts - who is exerting the force and on whom is the force being
exerted. The length of the arrows should represent qualitatively the magnitude of the force.
a)
c)
M
m
0
a
F
M
m
0
A block of mass m rests on a frictionless wedge which has a mass M and whose surface makes an angle to the horizontal as
Calculator

Transcribed Image Text:Make sure that each force arrow is labeled with two subscripts - who is exerting the force and on whom is the force being
exerted. The length of the arrows should represent qualitatively the magnitude of the force.
a)
M
m
0
Submit
a
c)
F
M
m
A block of mass m rests on a frictionless wedge which has a mass M and whose surface makes an angle to the horizontal as
shown. An external force F is acting on the wedge causing it to move to the right with constant acceleration.
a) Find the acceleration to the right such that the block m remains stationary relative to the wedge. Express your answer in
terms of m, 0, g, and M, as needed.
b) Describe qualitatively the motion of the block if the wedge had a greater acceleration than the one obtained in a).
c) What is the magnitude of the force F for which the two objects move with the same acceleration as in part a)? Express your
answer in terms of m, 0, g, and M, as needed.
In your solution, clearly indicate the coordinate axes you will use to write the forces. Include all the relevant free body diagrams and
label the forces with double subscript notation.
Calculator
Expert Solution
Step 1
(a)
Draw the free-body diagram of the system.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY