A local hospital has records of 130 patients who visited the emergency room with a variety of symptoms, including high blood pressure, respiratory problems, and abdominal pain. Their records show that • 71 had high blood pressure• 51 had respiratory problems• 39 had abdominal pain• 26 had high blood pressure and respiratory problems • 20 had high blood pressure and abdominal pain• 75 had respiratory problems or abdominal pain• 12 had all three symptoms a) Using these statistics, what is the probability that a random selection of one medical record will show that the patient had none of these three symptoms? b) Using these statistics, what is the probability that a random selection of one medical record will show that the patient had exactly one of the three symptoms?
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
A local hospital has records of 130 patients who visited the emergency room with a variety of symptoms, including high blood pressure, respiratory problems, and abdominal pain. Their records show that
• 71 had high blood pressure
• 51 had respiratory problems
• 39 had abdominal pain
• 26 had high blood pressure and respiratory problems • 20 had high blood pressure and abdominal pain
• 75 had respiratory problems or abdominal pain
• 12 had all three symptoms
a) Using these statistics, what is the
b) Using these statistics, what is the probability that a random selection of one medical record will show that the patient had exactly one of the three symptoms?
Given
Total patients who visited emergency room n(total) = 130
number of patients with high blood pressure n(BP) = 71
number of patients with respiratory problems n(R) = 51
number of patients with abdominal pain N(A) = 39
number of patients with high blood pressure and respiratory problems n(BP ∩ R) = 26
number of patients with high blood pressure and abdominal pain n(BP ∩ A) = 20
number of patients with respiratory problems or abdominal pain n(R U A) = 75
number of patients with all three symptoms = 12
a)
The number of patients with respiratory problems and abdominal pain are calculated as shown below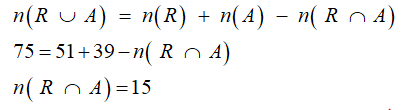
The total number of patients with high blood pressure or respiratory problems or abdominal pain should be calculated as shown below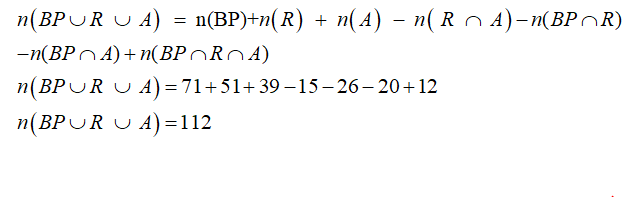
The number of patients with neither of three symptoms is calculated as shown below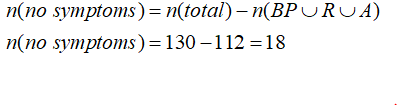
The probability that a random selection of one medical record will show that the patient had none of these three symptoms = 18/130 = 0.1385 (rounded to 4 decimals).
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images









