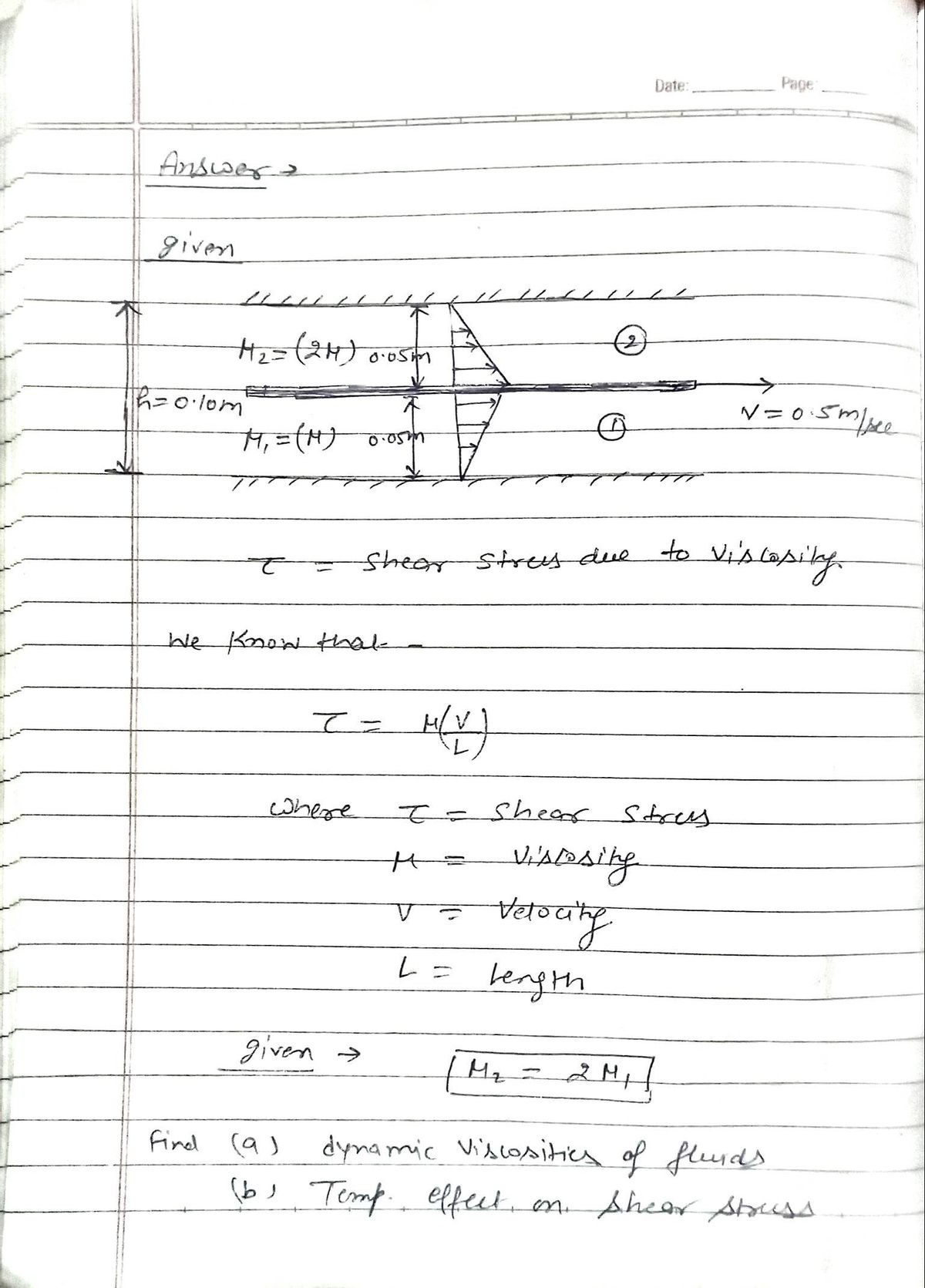
A large horizontal plate with finite thickness is located between two infinite walls, with two different fluids on each side. The viscosity of the fluid on the top of the plate is twice that of the fluid on the bottom of the plate. If the plate is pulled through the gap at a velocity (V) of 0.5 m/s, the resultant force on 1 m² of the plate due to the viscous shear on both sides is 30 N. The distance between the two infinite walls (h) is 0.10 m. Neglect all end effects, assume viscous flow and a linear velocity profile for the fluids. < h Top Wall Top Fluid Bottom Fluid Bottom Wall (a) Calculate the dynamic viscosities of the two fluids, assuming they are Newtonian. (b) If the fluids were heated, would you expect the shear stress to go up or down? Why? V
A large horizontal plate with finite thickness is located between two infinite walls, with two different fluids on each side. The viscosity of the fluid on the top of the plate is twice that of the fluid on the bottom of the plate. If the plate is pulled through the gap at a velocity (V) of 0.5 m/s, the resultant force on 1 m² of the plate due to the viscous shear on both sides is 30 N. The distance between the two infinite walls (h) is 0.10 m. Neglect all end effects, assume viscous flow and a linear velocity profile for the fluids. < h Top Wall Top Fluid Bottom Fluid Bottom Wall (a) Calculate the dynamic viscosities of the two fluids, assuming they are Newtonian. (b) If the fluids were heated, would you expect the shear stress to go up or down? Why? V
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A large horizontal plate with finite thickness is located
between two infinite walls, with two different fluids on
each side. The viscosity of the fluid on the top of the
plate is twice that of the fluid on the bottom of the
plate. If the plate is pulled through the gap at a velocity
(V) of 0.5 m/s, the resultant force on 1 m² of the plate
due to the viscous shear on both sides is 30 N. The
distance between the two infinite walls (h) is 0.10 m.
Neglect all end effects, assume viscous flow and a
linear velocity profile for the fluids.
<
Top Wall
Top Fluid
Bottom Fluid
Bottom Wall
(a) Calculate the dynamic viscosities of the two fluids, assuming they are Newtonian.
(b) If the fluids were heated, would you expect the shear stress to go up or down? Why?
V
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning