A B Draw an ellipse on the grid above. Have the piece of paper on a piece of cardboard backing. Put thumbtacks or pushpins through the foci of your ellipse (the two black dots). Tie a loop of string goes around the thumbtacks and, when stretched tight, does not go beyond the right and left- hand-sides of the grid. Keeping the string taut around the thumbtacks and making sure it does not slip, draw the ellipse with a pencil,. that 1. Use a ruler to measure the lengths of the axes on your ellipse in cm or mm. Write down the lengths (& units): a. minor axis: b. semiminor axis: c. major axis: d. semi-major axis:_ (Review what the previous page says about the importance of the semi-major axis.) 3 What is the
A B Draw an ellipse on the grid above. Have the piece of paper on a piece of cardboard backing. Put thumbtacks or pushpins through the foci of your ellipse (the two black dots). Tie a loop of string goes around the thumbtacks and, when stretched tight, does not go beyond the right and left- hand-sides of the grid. Keeping the string taut around the thumbtacks and making sure it does not slip, draw the ellipse with a pencil,. that 1. Use a ruler to measure the lengths of the axes on your ellipse in cm or mm. Write down the lengths (& units): a. minor axis: b. semiminor axis: c. major axis: d. semi-major axis:_ (Review what the previous page says about the importance of the semi-major axis.) 3 What is the
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Chapter1: The Study Of Minerals
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1LR
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A
B
Draw an ellipse on the grid above. Have the piece of paper on a piece of cardboard backing. Put
thumbtacks or pushpins through the foci of your ellipse (the two black dots). Tie a loop of string
that goes around the thumbtacks and, when stretched tight, does not go beyond the right and left-
hand-sides of the grid. Keeping the string taut around the thumbtacks and making sure it does not
slip, draw the ellipse with a pencil,.
1. Use a ruler to measure the lengths of the axes on your ellipse in cm or mm.
Write down the lengths (& units): a. minor axis:
b. semiminor axis:
c. major axis:
d. semi-major axis:
(Review what the previous page says about the importance of the semi-major axis.)
3. What is the average distance from the ellipse to one of its foci?
Draw a straight line from the Sun (left focus, black dot) towards the letter A, stopping your line
from the Sun where it hits the ellipse. Do the same with a line from the Sun towards the letter B
(do not draw the line past the ellipse). The area in-between your two lines is a "swept area."
Lightly shade in your swept area (using a pencil, not a pen.)
4. What is the area of your swept area, in terms of grid squares?
grid squares
Draw another line from the Sun (left-hand focus dot) to the aphelion, the point on the ellipse
farthest from the Sun, on the right. Make that the beginning of a second swept area equal to the
first swept area.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Introduction
The task is to draw the elips by string and pin method, and from which to determine the length of major, minor axis, semi major and semi minor axis.
Major axis is the longest dimeter which runs through the center of each focii.
Th semi major axis is the diameter which run from the center through focus to perimeter.
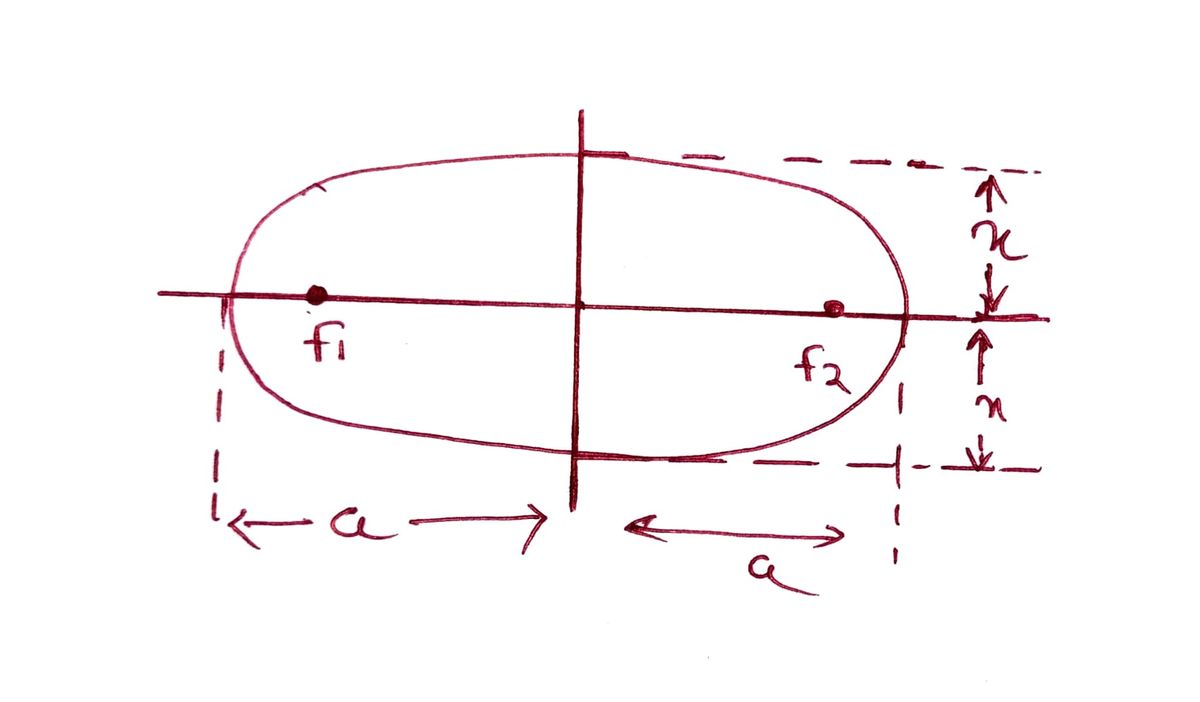
2a is the length of the major axis and a is the length of the semi-major axis.
2x is the length of the minor axis and X is the length of semi-minor axis.
“Since you have posted a question with multiple sub parts, we will provide the solution only to the first three sub parts as per our Q&A guidelines. Please repost the remaining sub parts separately.”
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science …
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134746241
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134041360
Author:
Greg Carbone
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781260153125
Author:
William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science …
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134746241
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134041360
Author:
Greg Carbone
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781260153125
Author:
William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134543536
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781337569613
Author:
G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781259916823
Author:
Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,