Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
a 500g sample of. water at 53 degree celsius is cooled down "-7" degree. celsius how much energy is removed

Transcribed Image Text:**Graph and Model Descriptions:**
**B3. Use a graph to depict changes in temperature over time. (Graph)**
The graph illustrates temperature changes over time. It includes various segments: an inclined line marked "th," a horizontal line labeled "ph," and another inclined line marked "th." These segments likely represent heating phases with temperature increases (th) and a phase change at constant temperature (ph). The y-axis is labeled "-7," suggesting a temperature scale, and the x-axis represents time.
**A3. Use a graphical model to show how energy is conserved during a series of phase changes. (LOL)**
The graphical model includes a series of representations showing energy conservation:
- Alternating symbols of rectangles and circles suggest different states of matter or energy levels.
- Arrows indicate transitions between these states, possibly representing energy flow or phase changes.
**Calculation Section:**
**B1. Calculate the amount of energy transferred for a change in temperature.**
Includes the variables "500g" (likely referring to the mass of a substance) used for calculating energy transferred during a temperature change.
**B2. Calculate the amount of energy transferred for a change in phase.**
This section is left open for calculations regarding energy transfer during a phase change.
**Descriptive Section:**
**A2. Describe how changes in energy at the macroscopic level affect the motion and arrangement of particles. (Particle Diagram)**
The section is intended for explaining the effects of energy changes on particle motion and arrangement, with space left for a particle diagram to illustrate these concepts.
This content is designed to guide students in understanding thermal and phase energy concepts through visual and computational analysis.
Expert Solution
Step 1
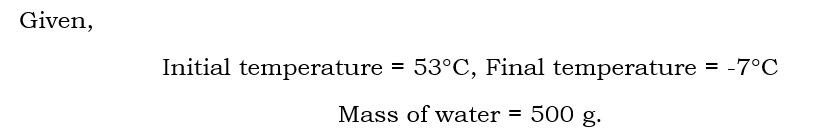
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY