College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
![The vectors are defined as follows:
\[
\vec{A} = 3\hat{i} + 4\hat{j}, \quad \vec{B} = \hat{i} + 2\hat{j}
\]
- **Vector \(\vec{A}\):** Consists of a component of 3 along the \( \hat{i} \) axis (horizontal) and 4 along the \( \hat{j} \) axis (vertical).
- **Vector \(\vec{B}\):** Consists of a component of 1 along the \( \hat{i} \) axis and 2 along the \( \hat{j} \) axis.
These vectors are expressed in the standard unit vector notation, where \( \hat{i} \) represents the unit vector in the horizontal direction and \( \hat{j} \) represents the unit vector in the vertical direction.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F284c643e-4e72-49d0-b15d-09efe1795f03%2Fb468438f-fad8-4242-92b7-a7986de4ad98%2Feogst5k_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:The vectors are defined as follows:
\[
\vec{A} = 3\hat{i} + 4\hat{j}, \quad \vec{B} = \hat{i} + 2\hat{j}
\]
- **Vector \(\vec{A}\):** Consists of a component of 3 along the \( \hat{i} \) axis (horizontal) and 4 along the \( \hat{j} \) axis (vertical).
- **Vector \(\vec{B}\):** Consists of a component of 1 along the \( \hat{i} \) axis and 2 along the \( \hat{j} \) axis.
These vectors are expressed in the standard unit vector notation, where \( \hat{i} \) represents the unit vector in the horizontal direction and \( \hat{j} \) represents the unit vector in the vertical direction.

Transcribed Image Text:The text contains mathematical notations related to vectors:
1. **|**\(\vec{A}\)**|** - The magnitude of vector \(\vec{A}\).
2. **\(\vec{A} + \vec{B}\)** - The sum of vectors \(\vec{A}\) and \(\vec{B}\).
3. **\(\vec{A} - \vec{B}\)** - The difference between vectors \(\vec{A}\) and \(\vec{B}\).
4. **\(\vec{A} \cdot \vec{B}\)** - The dot product of vectors \(\vec{A}\) and \(\vec{B}\).
5. **\(\vec{A} \times \vec{B}\)** - The cross product of vectors \(\vec{A}\) and \(\vec{B}\).
These are fundamental operations in vector algebra, used in physics and engineering to solve problems involving direction and magnitude.
Expert Solution
Step 1
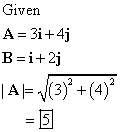
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON