A) 1.26 B) 3.02 C) 0.612 21) Which one of these statements about strong base is true A) Strong bases produce solutions with a higher pH than weak bases B) Bases have only the OH group in their structure C) Strong bases are very concentrated acids D) Strong bases are 100% ionized in water D) 1.96 22) Consider the reaction represented by the equation: Fe (aq) + SCN (aq) → FeSCN²+ (aq) 6.00 M Fe³+ (aq) and 10.0 M SCN (aq) are mixed at a certain temperature and at equilibrium the concentration of FeSCN2+ (aq) is 2.50 M. A) 295x10-3 B) 303 x104 C) 250x104 D) 95 x10³
Ionic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium are two major concepts in chemistry. Ionic equilibrium deals with the equilibrium involved in an ionization process while chemical equilibrium deals with the equilibrium during a chemical change. Ionic equilibrium is established between the ions and unionized species in a system. Understanding the concept of ionic equilibrium is very important to answer the questions related to certain chemical reactions in chemistry.
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius acid act as a good electrolyte as it dissociates to its respective ions in the aqueous solutions. Keeping it similar to the general acid properties, Arrhenius acid also neutralizes bases and turns litmus paper into red.
Bronsted Lowry Base In Inorganic Chemistry
Bronsted-Lowry base in inorganic chemistry is any chemical substance that can accept a proton from the other chemical substance it is reacting with.
![79
13) A solution was made by dissolving 4.05 g of a solute in 130:9 g of acetone. The solution boiled at 56.58°
C. The boiling point of pure acetone is 55.95° C, and the Ks-1.71° C/m. What is the molecular weight
of the solute?
A) 80.3
B) 105
C) 12.7
D) 140
14) The decomposition of N₂Os(g)-NO2(g) + NO3(g) proceeds as a first order reaction with a half-life of
30.0 seconds at a certain temperature. If the initial concentration [N:Oslo 0.400 M, what is the
concentration after 150 seconds?
A) 0.400 M
B) 0.100 M
C) 0.025 M
D) 0.013 M
15) Which equation below best gives the concentration of N₂Os versus time in the previous question Q14?
A) [N₂0s] ([N2Oslo)/t12 B) [N20₁] - kt
C) [N20s]-[N2Osloe D) 1/[N20s] =1/[N20s]+ kt
T
16) The rate constant for the first order reaction A---> B+C is k-2.2 x 10 min-¹ at 57 K. What is the
half-life for this reaction at 57 K?
A) 9.1 min
D) 1200 min
B) 32 min
17) Calculate AH° for the reaction: 2C) + 2H₂O) --->
->
C(s) + H₂O
H2(g) + CO2(g)
CH4) + H₂O(g)
(1) CO(g) + H₂(g)
(2) CO(g) + H₂O(g) --->
(3) CO(g) + 3H2(g) --->
C) 64 min
CH4(g) + CO2(g)
AH-150 kJ
AH-41kJ
ΔΗ°==-206}J
A) 53 kJ
B) 116 kJ
C) -372 kJ
D)-116 kJ
18) When a strong acid is titrated with a weak base, the pH at the equivalence point is ALWAYS
A) <7
B) 7
9>7
D) <1
19) Which is the weakest intermolecular force among a group of molecules of comparable molar mass?
A) Dipole-dipole
B) London
C) Ionic bonding
D) Hydrogen bonding
20)
Given: N2(g) + 3 H₂(g) <-> 2 NH3(g)
At equilibrium at a certain temperature, the concentration of NH3(g), H₂(g) and N₂(g) are 0.490 M, 1.41 M
and 0.14 M, respectively. Calculate the value of Ke for this reaction.
A) 1.26
B) 3.02
C) 0.612
D) 1.96
21) Which one of these statements about strong base is true
A) Strong bases produce solutions with a higher pH than weak bases
B) Bases have only the OH group in their structure
C) Strong bases are very concentrated acids
D) Strong bases are 100% ionized in water
22) Consider the reaction represented by the equation: Fe³+ (aq) + SCN- (aq) → FeSCN²+ (aq)
6.00 M Fe³+ (aq) and 10.0 M SCN (aq) are mixed at a certain temperature and at equilibrium
the concentration of FeSCN2+ (aq) is 2.50 M.
A) 295x10-3
B) 303 x104
D) 95 x10³
C) 250x104
23) Consider the following reaction: 4 PCB(g)-> P4(g) + 6 Cl2(g)
If the initial concentration of PC13(g) is 3.0 M, and "x" is the equilibrium concentration of P4(g), what is the
correct equilibrium relation?
A) Kc = 6x7
B) Kc=6x7/(3.0-x)+
D) Kc=x7/(3.0-x)*
C) Kc = (x)(6x)/(3.0-4x)*
24) What is the density of NH3 at 5 atm pressure and a temperature of 35°C?
C) 0.980 g/L
B) 3.36 g/L
A) 16.6 g/L
25) What is the pH of 80.0 M aqueous solution of NH3 (ammonia). It's Kb = 1.8 x 10³.
B) 1.98
A)12.6
C) 0.778
D) 1.39 g/L
D) 0.0104
CAS](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F48079d7c-7248-4f29-b2fc-02e5764ca6aa%2F57441488-f776-49a6-8a64-20068c2af822%2Feijdijk_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
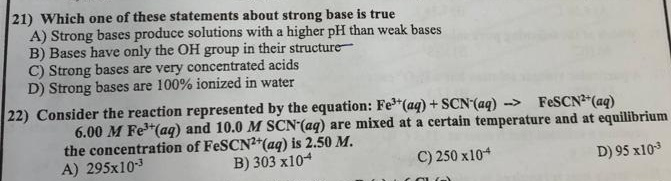
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images









