9Tt sin 8. Find the exact value of: sin
Correlation
Correlation defines a relationship between two independent variables. It tells the degree to which variables move in relation to each other. When two sets of data are related to each other, there is a correlation between them.
Linear Correlation
A correlation is used to determine the relationships between numerical and categorical variables. In other words, it is an indicator of how things are connected to one another. The correlation analysis is the study of how variables are related.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical method in which it estimates the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variable. In simple terms dependent variable is called as outcome variable and independent variable is called as predictors. Regression analysis is one of the methods to find the trends in data. The independent variable used in Regression analysis is named Predictor variable. It offers data of an associated dependent variable regarding a particular outcome.
![**Problem**
2) Find the exact value of:
\[
\sin^{-1} \left[ \sin \left( \frac{9\pi}{8} \right) \right].
\]
**Solution**
The function \(\sin^{-1}(x)\), also known as arcsin, returns the angle \(\theta\) in the range \([- \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}]\) such that \(\sin(\theta) = x\).
To solve \(\sin^{-1} \left[ \sin \left( \frac{9\pi}{8} \right) \right]\), we must first determine the angle whose sine is equal to \(\sin \left( \frac{9\pi}{8} \right)\) and that lies within the principal range of arcsin.
First, observe that:
1. \(\frac{9\pi}{8}\) is greater than \(\pi\) and less than \(\frac{3\pi}{2}\). This means \(\frac{9\pi}{8}\) lives in the third quadrant, where sine is negative.
2. The reference angle corresponding to \(\frac{9\pi}{8}\) is \(\frac{9\pi}{8} - \pi = \frac{\pi}{8}\).
3. Since sine has a period of \(2\pi\), the sine value of \(\frac{9\pi}{8}\) is negative and equals \(-\sin \left( \frac{\pi}{8} \right)\).
We need an equivalent angle within \([- \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}]\) that has the same sine value. As \(\sin \left( \frac{9\pi}{8} \right) = -\sin \left( \frac{\pi}{8} \right)\),
- The angle with sine \(-\sin \left( \frac{\pi}{8} \right)\) in the range \([- \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}]\) is \(-\frac{\pi}{8}\).
Therefore,
\[
\sin^{-1} \left[ \sin \left( \frac{9\pi}{8} \right) \right] = -\frac{\pi}{8}.
\](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ff5445541-3bd8-48a0-bfe5-5b2c37f58de6%2F226a3c87-0821-4c17-9a49-6462e18a8aea%2Fijtb2qq_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Given:
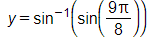
The inverse sine function is defined in the interval .
From the above expression,
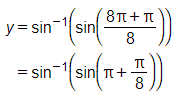
The angle lies in the 3rd quadrant, where the value of the sine function is negative.
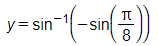
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 6 images







