8) Can this program have no effect on labor supply? If yes show how graphically. h) Can this program decrease labor supply? (Hint some current workers are eligible for DI but choose to work instead) Explain how it possible or impossible. If possible show how graphically.
q3. g h
thank you

the social security disability insurance(DI) program was restructured so that the disabled could get disability benefits if they were not able to get any job or they don't earn any labour wages. Accordingly they were paid $500 but a condition that if they are employed and start earning any benefit out of their labour work then their DI benefit of $500 would be immediately cancelled out.
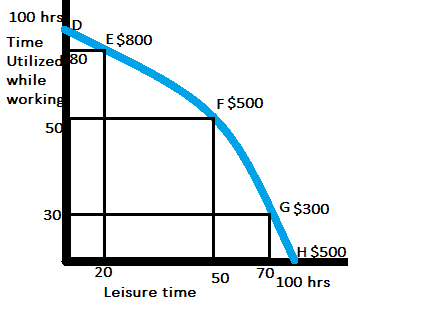
Here a disabled has a choice between 100 hours of labour or 100 hours of leisure. If a person chooses 100 hours of leisure then he would get DI benefit of $500. But if the disabled even chooses to work for even 1 hour then he gains $10 but losses $500 of DI benefit. So, naturally the disabled has to work for 50 hours to gain as much as what a disabled without work gains.
Here the congress being concerned about the disabled and the work disincentives in this program, the relevant committee proposed two alternatives:-
alternative A:-reduction of DI benefit from $500 to $300
Alternative B:- if a disabled doesn't works then he gains $500. But if a disabled works then he gains $300 with a condition that he should not earn more than $300 as labour benefits.
Here alternative B provides a better plan whereby if a disabled worker works for 30 hours then he/she gains $300 as labour benefits and in addition to $300 as DI benefit. The total earning here is $600 as against the unemployed disabled who is earning $500.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images









