779?module_item_id=965486 Let X = the number of years a new hire will stay with the company. Let P(x) = the probability that a new hire will stay with the company x years. Complete probability distribution table using the data provided. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 On(x<2) X acer 0.09 0.14 0.08 0.1 0.12 0.11 P(x) (a) What notation would you use for finding the probability that a new hire will stay with the company for 2? Op(x>2) Op(x-2) Op(x<2) (b) What notation would you use for finding the probability that a new hire will stay with the company for less than 2 years? < W Sep 20 12:55 0 home
779?module_item_id=965486 Let X = the number of years a new hire will stay with the company. Let P(x) = the probability that a new hire will stay with the company x years. Complete probability distribution table using the data provided. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 On(x<2) X acer 0.09 0.14 0.08 0.1 0.12 0.11 P(x) (a) What notation would you use for finding the probability that a new hire will stay with the company for 2? Op(x>2) Op(x-2) Op(x<2) (b) What notation would you use for finding the probability that a new hire will stay with the company for less than 2 years? < W Sep 20 12:55 0 home
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Don’t know how to solve

Transcribed Image Text:779?module_item_id=965486
Let X = the number of years a new hire will stay with the company.
Let P(x) = the probability that a new hire will stay with the company x years.
Complete probability distribution table using the data provided.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
On(x<2)
X
acer
0.09
0.14
0.08
0.1
0.12
0.11
P(x)
(a) What notation would you use for finding the probability that a new hire will stay with the company for 2?
Op(x>2)
Op(x-2)
Op(x<2)
(b) What notation would you use for finding the probability that a new hire will stay with the company for less
than 2 years?
راء
W
<
Sep 20
page up
12:55
page dn
0
home
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Part 2
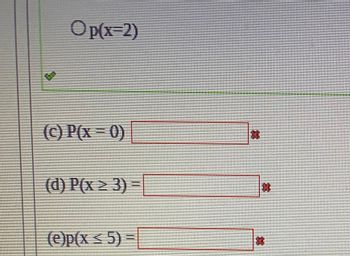
Transcribed Image Text:Op(x-2)
(c) P(x=0)
(d) P(x ≥ 3) =
(e)p(x ≤ 5) =
EDE
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman