7. If f(x) = ve find the values of x that satisfy the inequality f (x) < 0. Find the critical %3D x2-16 numbers and use the number line to find the solution set and write the solution set in interval notation. Interval Notation:
7. If f(x) = ve find the values of x that satisfy the inequality f (x) < 0. Find the critical %3D x2-16 numbers and use the number line to find the solution set and write the solution set in interval notation. Interval Notation:
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN:9780134463216
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:Robert F. Blitzer
ChapterP: Prerequisites: Fundamental Concepts Of Algebra
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1MCCP: In Exercises 1-25, simplify the given expression or perform the indicated operation (and simplify,...
Related questions
Question
![**Problem Statement:**
7. If \( f(x) = \frac{1}{x^2 - 16} \), find the values of \( x \) that satisfy the inequality \( f(x) < 0 \). Find the critical numbers and use the number line to find the solution set and write the solution set in interval notation.
**Graph/Diagram Explanation:**
The image contains a horizontal number line with arrows pointing both left and right, indicating a continuous line. There are no markings or intervals shown on the number line in the image.
**Solution Steps:**
1. **Function and Inequality Analysis:**
\[
f(x) = \frac{1}{x^2 - 16}
\]
The expression is undefined for values of \( x \) where \( x^2 - 16 = 0 \). Solving \( x^2 - 16 = 0 \) gives:
\[
x^2 = 16 \quad \Rightarrow \quad x = \pm 4
\]
These are the critical numbers which make the denominator zero.
2. **Sign Analysis of the Inequality:**
The inequality \( \frac{1}{x^2 - 16} < 0 \) requires \( x^2 - 16 \) to be negative:
\[
x^2 - 16 < 0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad (x-4)(x+4) < 0
\]
Use test points or a sign chart to determine intervals where the product is negative:
- Using test points such as \( x = 0 \), \( x = -5 \), and \( x = 5 \).
- Interval \((-4, 4)\) makes the inequality true because between these values, one factor is negative and one is positive.
3. **Interval Notation:**
\((-4, 4)\)
In this context, \( (-4, 4) \) is the solution set where the inequality \( f(x) < 0 \) holds true. The interval notation signifies all \( x \)-values between \(-4\) and \(4\) where the expression is negative.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fc7c25342-3eba-4907-89b6-b77dd86de917%2Fa3bd65c5-e8cd-4964-8248-e10bdee32d71%2Fyz1ehn_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
7. If \( f(x) = \frac{1}{x^2 - 16} \), find the values of \( x \) that satisfy the inequality \( f(x) < 0 \). Find the critical numbers and use the number line to find the solution set and write the solution set in interval notation.
**Graph/Diagram Explanation:**
The image contains a horizontal number line with arrows pointing both left and right, indicating a continuous line. There are no markings or intervals shown on the number line in the image.
**Solution Steps:**
1. **Function and Inequality Analysis:**
\[
f(x) = \frac{1}{x^2 - 16}
\]
The expression is undefined for values of \( x \) where \( x^2 - 16 = 0 \). Solving \( x^2 - 16 = 0 \) gives:
\[
x^2 = 16 \quad \Rightarrow \quad x = \pm 4
\]
These are the critical numbers which make the denominator zero.
2. **Sign Analysis of the Inequality:**
The inequality \( \frac{1}{x^2 - 16} < 0 \) requires \( x^2 - 16 \) to be negative:
\[
x^2 - 16 < 0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad (x-4)(x+4) < 0
\]
Use test points or a sign chart to determine intervals where the product is negative:
- Using test points such as \( x = 0 \), \( x = -5 \), and \( x = 5 \).
- Interval \((-4, 4)\) makes the inequality true because between these values, one factor is negative and one is positive.
3. **Interval Notation:**
\((-4, 4)\)
In this context, \( (-4, 4) \) is the solution set where the inequality \( f(x) < 0 \) holds true. The interval notation signifies all \( x \)-values between \(-4\) and \(4\) where the expression is negative.
Expert Solution
Step 1
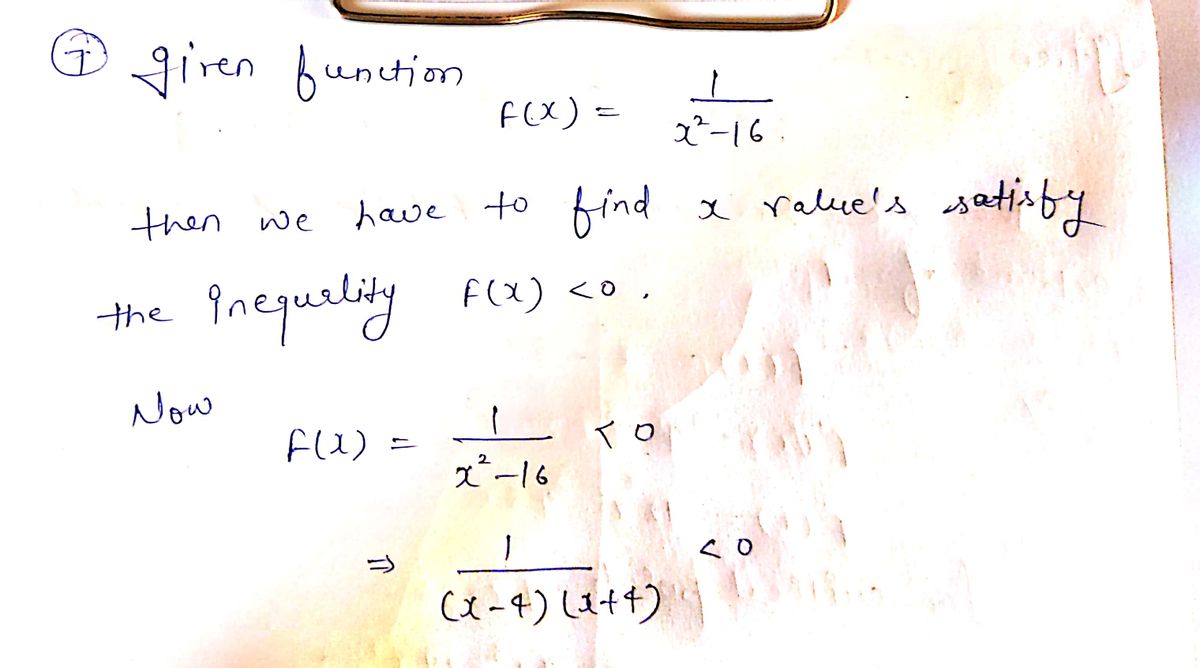 Tt
Tt
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780134463216
Author:
Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:
PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305657960
Author:
Joseph Gallian
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780134463216
Author:
Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:
PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305657960
Author:
Joseph Gallian
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780135163078
Author:
Michael Sullivan
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth Edition
Algebra
ISBN:
9780980232776
Author:
Gilbert Strang
Publisher:
Wellesley-Cambridge Press

College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780077836344
Author:
Julie Miller, Donna Gerken
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education