7. A population has u = 60 and o = 10. Find the z-score corresponding to each of the following sample means: a. A sample of n = 4 with M = 55 b. A sample of n = 25 with M = 55 C. A sample of n = 100 with M = 55 d. What do we notice about the z-scores as the sample size changes %3D
7. A population has u = 60 and o = 10. Find the z-score corresponding to each of the following sample means: a. A sample of n = 4 with M = 55 b. A sample of n = 25 with M = 55 C. A sample of n = 100 with M = 55 d. What do we notice about the z-scores as the sample size changes %3D
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Rounding policy:
- Proportion: 4 decimal places
- Percentile: round to the closest whole unit number
- All others: 2 decimal places

Transcribed Image Text:### Problem 7
A population has \( \mu = 60 \) and \( \sigma = 10 \). Find the z-score corresponding to each of the following sample means:
a. A sample of \( n = 4 \) with \( M = 55 \)
b. A sample of \( n = 25 \) with \( M = 55 \)
c. A sample of \( n = 100 \) with \( M = 55 \)
d. What do we notice about the z-scores as the sample size changes?
### Problem 8
If you are taking a random sample from a normal population with \( \mu = 100 \) and \( \sigma = 16 \), which of the following outcomes is more likely? Explain your answer.
a. A sample mean greater than 106 for a sample of \( n = 4 \).
b. A sample mean greater than 103 for a sample of \( n = 36 \).
![**Study on the Effectiveness of Relaxation Training in Reducing Anxiety**
A researcher evaluated the effectiveness of relaxation training in reducing anxiety. One sample of anxiety-ridden people received relaxation training, while a second sample did not. Then anxiety scores were measured for all subjects using a standardized test. Use the information summarized in the following table to complete this item.
**Table: The Effect of Relaxation Training on Anxiety Scores**
| Group | Mean Anxiety Score | SE (Standard Error) |
|---------------------|--------------------|---------------------|
| Control group | 36 | 7 |
| Relaxation training | 18 | 5 |
**Questions:**
a. **What is the independent variable (IV)?**
- The independent variable is the type of group (Control group vs. Relaxation training).
b. **How many levels do we have for the IV?**
- There are two levels for the independent variable: Control group and Relaxation training.
c. **What is the level of measurement for the IV?**
- The level of measurement for the IV is nominal (categorical).
d. **What is the DV (dependent variable, remember, the DV is the data)?**
- The dependent variable is the Mean Anxiety Score.
e. **What is the level of measurement of the DV?**
- The level of measurement for the DV is interval.
f. **What is the best graph to display this data? Explain.**
- A bar graph would be the best way to display this data as it allows comparison of mean anxiety scores between two categorical groups with their respective standard errors.
g. **Construct a graph (by hand) that incorporates all the information in this table.**
- [Instructions for creating a bar graph: Draw two bars, one for each group. Label the y-axis with mean anxiety scores ranging from 0 to 40. Place the control group at a mean score of 36 with an error bar extending from 29 to 43. Place the relaxation training group at a mean score of 18 with an error bar extending from 13 to 23.]
h. **Looking at your graph, do you think that the relaxation training really worked? Explain your answer.**
- Based on the graph, relaxation training appears to be effective in reducing anxiety as the mean anxiety score for the relaxation training group is substantially lower than for the](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe39e6f31-fb38-4df4-8e11-f23a384cb477%2F65b7ca00-4f5a-40bd-9c18-c053a7cc65db%2Fzxox7ic_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Study on the Effectiveness of Relaxation Training in Reducing Anxiety**
A researcher evaluated the effectiveness of relaxation training in reducing anxiety. One sample of anxiety-ridden people received relaxation training, while a second sample did not. Then anxiety scores were measured for all subjects using a standardized test. Use the information summarized in the following table to complete this item.
**Table: The Effect of Relaxation Training on Anxiety Scores**
| Group | Mean Anxiety Score | SE (Standard Error) |
|---------------------|--------------------|---------------------|
| Control group | 36 | 7 |
| Relaxation training | 18 | 5 |
**Questions:**
a. **What is the independent variable (IV)?**
- The independent variable is the type of group (Control group vs. Relaxation training).
b. **How many levels do we have for the IV?**
- There are two levels for the independent variable: Control group and Relaxation training.
c. **What is the level of measurement for the IV?**
- The level of measurement for the IV is nominal (categorical).
d. **What is the DV (dependent variable, remember, the DV is the data)?**
- The dependent variable is the Mean Anxiety Score.
e. **What is the level of measurement of the DV?**
- The level of measurement for the DV is interval.
f. **What is the best graph to display this data? Explain.**
- A bar graph would be the best way to display this data as it allows comparison of mean anxiety scores between two categorical groups with their respective standard errors.
g. **Construct a graph (by hand) that incorporates all the information in this table.**
- [Instructions for creating a bar graph: Draw two bars, one for each group. Label the y-axis with mean anxiety scores ranging from 0 to 40. Place the control group at a mean score of 36 with an error bar extending from 29 to 43. Place the relaxation training group at a mean score of 18 with an error bar extending from 13 to 23.]
h. **Looking at your graph, do you think that the relaxation training really worked? Explain your answer.**
- Based on the graph, relaxation training appears to be effective in reducing anxiety as the mean anxiety score for the relaxation training group is substantially lower than for the
Expert Solution
Step 1
“Since you have asked multiple question, we will solve the first question for you. If you
want any specific question to be solved then please specify the question number or post
only that question"
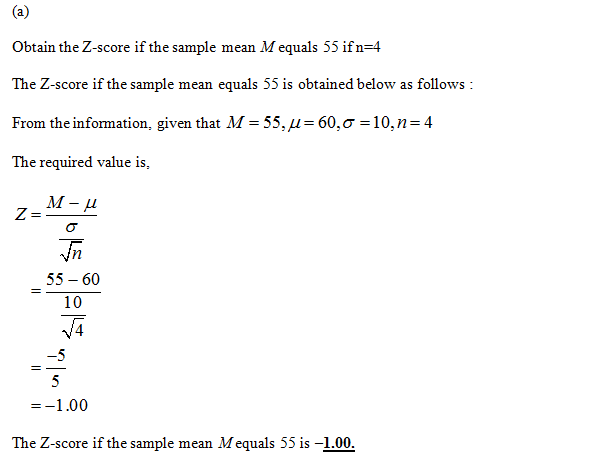
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman