Analyzing Infrared Spectra
The electromagnetic radiation or frequency is classified into radio-waves, micro-waves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays. The infrared spectra emission refers to the portion between the visible and the microwave areas of electromagnetic spectrum. This spectral area is usually divided into three parts, near infrared (14,290 – 4000 cm-1), mid infrared (4000 – 400 cm-1), and far infrared (700 – 200 cm-1), respectively. The number set is the number of the wave (cm-1).
IR Spectrum Of Cyclohexanone
It is the analysis of the structure of cyclohexaone using IR data interpretation.
IR Spectrum Of Anisole
Interpretation of anisole using IR spectrum obtained from IR analysis.
IR Spectroscopy
Infrared (IR) or vibrational spectroscopy is a method used for analyzing the particle's vibratory transformations. This is one of the very popular spectroscopic approaches employed by inorganic as well as organic laboratories because it is helpful in evaluating and distinguishing the frameworks of the molecules. The infra-red spectroscopy process or procedure is carried out using a tool called an infrared spectrometer to obtain an infrared spectral (or spectrophotometer).
do a IR spectra analysis and draw the molecular structure. Provide a well-explained solution.

The NMR spectrum provides the following details about the structure of the molecules:
- The number of signals: The number of signals gives information about the different types of hydrogen atoms.
- Position of signal: The position of the signal tells us about the electronic environment of hydrogen.
- splitting of signal: Splitting of the signal tells us about the number of neighboring hydrogen atom present. If the number of the neighboring hydrogen atom is n then the signal split in (n+1) peak.
- Area of signal: The area of the signal provides information about the number of hydrogen atoms responsible for the signal.
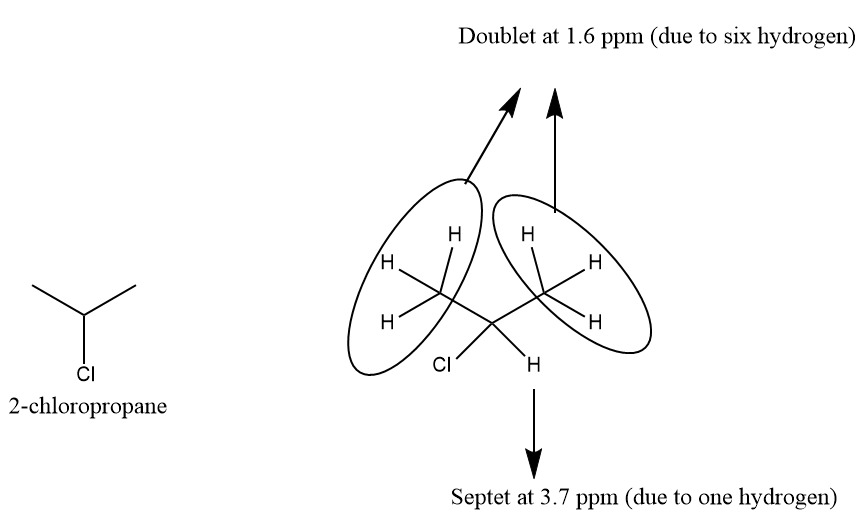
The given molecule gives two signals in the NMR spectrum and it confirms the presence of two types of the hydrogen atom in the molecules.
- Septet at 3.7 ppm due to one hydrogen with six neighbouring hydrogen (septet = (n+1) = 6+1 = 7).
- Doublet at 1.6 ppm is due to one hydrogen with one neighbouring hydrogen atom (doublet = (1+1) = 1+1 = 2).
The molecular formula of the compound is C3H7Cl. The total hydrogen atom in the molecule is seven. Seven hydrogen atoms divided into two sets (6+1). Six hydrogens are the same type confirms the presence of two CH3 groups attached with the same carbon.
On the basis of the above structure the structure of the compound is as follows:
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









