40° C
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Can you please solve number two

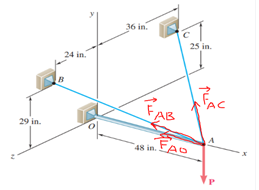
Transcribed Image Text:The image shows a mechanical problem involving a boom, cables, and a load. The boom OA carries a load \( P \) and is supported by two cables. The system is defined as follows:
1. The tension in cable AB is 183 lb.
2. The resultant of the load \( P \) and the forces exerted at point A by the two cables must be directed along OA.
The problem consists of two parts:
a) Determine the tension in cable AC.
b) Determine the magnitude of the load \( P \).
**Diagrams Explanation:**
There are two diagrams provided:
1. Top View:
- The boom is shown extending along the x-axis.
- Cable AB is attached to the boom at an angle of 40° to the horizontal plane.
- Cable AC is similarly attached but is situated in the z-direction, making angles with the x-axis and z-axis.
2. Side View:
- This diagram provides the lengths and angles of the cables.
- Cable AB connects to point B, located 24 in. along the z-axis and 29 in. along the x-axis from point A.
- Cable AC connects to point C, situated 36 in. along the y-axis and 25 in. along the z-axis from point A.
- Point A is connected to the load \( P \), positioned vertically downward, 48 in. beneath the z-plane.
The objective is to calculate the unknown tensions and the load magnitude by resolving the forces within the system.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Write the coordinates and postion vector-
The diagram of force vectors is given as,
The co-ordinate at point A,
The co-ordinate at point B,
The co-ordinate at point C,
The vector AB,
The unit vector in the direction of AB,
The force in the direction of AB is expressed as follows-
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 17 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY