4 m B B U =3.3 mi/s UR = 5.5 km/s 1600 mi Fig. P13.11 and P13.13* Fig. P13.12* and P13.14 4 Mm 13.13* and 13.14 shown, In the position S, it has an altitude as and a speed vs as indicated. When it passes through the point B, its speed is vg as indicated. Determine the altitude ar of A satellite describes an elliptic orbit around the earth as the point B. 13.15 Refer to Prob. 13.11. Determine the altitude ao of the apogee Q. Fig. P13.17 13.16 Refer to Prob. 13.12. Determine the altitude ao of the apogee Q. 1.25 m 13.17 and 13.18* A spring of free length 2.5 m and modulus 200 N/m is attached to a sliding collar C of mass 20 kg as shown. The collar is released from rest at A to slide downward. Neglecting effects of friction, determine the speed of the collar as it passes through B. 3 m
4 m B B U =3.3 mi/s UR = 5.5 km/s 1600 mi Fig. P13.11 and P13.13* Fig. P13.12* and P13.14 4 Mm 13.13* and 13.14 shown, In the position S, it has an altitude as and a speed vs as indicated. When it passes through the point B, its speed is vg as indicated. Determine the altitude ar of A satellite describes an elliptic orbit around the earth as the point B. 13.15 Refer to Prob. 13.11. Determine the altitude ao of the apogee Q. Fig. P13.17 13.16 Refer to Prob. 13.12. Determine the altitude ao of the apogee Q. 1.25 m 13.17 and 13.18* A spring of free length 2.5 m and modulus 200 N/m is attached to a sliding collar C of mass 20 kg as shown. The collar is released from rest at A to slide downward. Neglecting effects of friction, determine the speed of the collar as it passes through B. 3 m
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Question 13.18
(please do problem 13.18 and not 13.17 as it is posted as a seperate question)

Transcribed Image Text:4 m
B
U = 3.3 mi/s
UR = 5.5 km/s
1600 mi
Fig. P13.11 and P13.13*
Fig. P13.12* and P13.14
4 Mm
13.13 and 13.14
shown. In the position S, it has an altitude as and a speed vs as indicated. When it
passes through the point B, its speed is vB as indicated. Determine the altitude ag of
the point B.
13.15 Refer to Prob. 13.11. Determine the altitude
A satellite describes an elliptic orbit around the earth as
Fig. P13.17
of the apogee Q.
13.16 Refer to Prob. 13.12. Determine the altitude
of the apogee Q.
1.25 m
13.17 and 13.18* A spring of free length 2.5 m and modulus 200 N/m is attached
to a sliding collar C of mass 20 kg as shown. The collar is released from rest at A
to slide downward. Neglecting effects of friction, determine the speed of the collar
as it passes through B.
13.19 A spring of free length 10 m and modulus 120 N/m is attached to a sliding
collar C of mass 20 kg as shown. The collar is released from rest at A. Neglecting
effects of friction, determine the speed of the collar as it passes through B.
A
3 m
C
B
Fig. P13.18*
Expert Solution
Step 1
As I had uploaded P13.18 in previous one where 13.17 asked, I am uploading 13.17 here.
Given,
m = 20 kg
Free length = L = 2.5 m
Spring constant = k = 200 N/m
Consider below diagram to understand initial and final length of the spring:
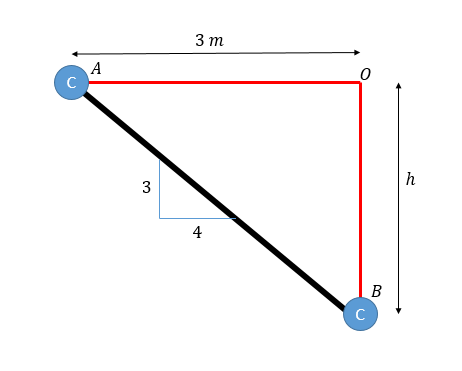
From the given triangle, we know that,
Initial length = L1 = OA = 3 m
Final length = L2 = OB = 4 m
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY