Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
![**Problem 3:** Solve the equation: \( x(2x + 7) = 4 \).
**Solution Steps:**
1. **Expand the Equation:**
\[
x(2x + 7) = 4 \implies 2x^2 + 7x = 4
\]
2. **Bring all terms to one side to form a quadratic equation:**
\[
2x^2 + 7x - 4 = 0
\]
3. **Solve the Quadratic Equation:**
To solve \(2x^2 + 7x - 4 = 0\), use the quadratic formula:
\[
x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}
\]
Where \(a = 2\), \(b = 7\), and \(c = -4\).
4. **Calculate the Discriminant:**
\[
b^2 - 4ac = 7^2 - 4(2)(-4) = 49 + 32 = 81
\]
5. **Apply the Quadratic Formula:**
\[
x = \frac{-7 \pm \sqrt{81}}{4} = \frac{-7 \pm 9}{4}
\]
6. **Find the Roots:**
- Positive Root:
\[
x = \frac{-7 + 9}{4} = \frac{2}{4} = \frac{1}{2}
\]
- Negative Root:
\[
x = \frac{-7 - 9}{4} = \frac{-16}{4} = -4
\]
**Conclusion:**
The solutions to the equation \( x(2x + 7) = 4 \) are \( x = \frac{1}{2} \) and \( x = -4 \).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fee88b8a7-c213-48e1-bed2-7c496e1303f2%2F2df0754a-88ef-4d9f-b81f-635edca6e909%2F2sj4nmf_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 3:** Solve the equation: \( x(2x + 7) = 4 \).
**Solution Steps:**
1. **Expand the Equation:**
\[
x(2x + 7) = 4 \implies 2x^2 + 7x = 4
\]
2. **Bring all terms to one side to form a quadratic equation:**
\[
2x^2 + 7x - 4 = 0
\]
3. **Solve the Quadratic Equation:**
To solve \(2x^2 + 7x - 4 = 0\), use the quadratic formula:
\[
x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}
\]
Where \(a = 2\), \(b = 7\), and \(c = -4\).
4. **Calculate the Discriminant:**
\[
b^2 - 4ac = 7^2 - 4(2)(-4) = 49 + 32 = 81
\]
5. **Apply the Quadratic Formula:**
\[
x = \frac{-7 \pm \sqrt{81}}{4} = \frac{-7 \pm 9}{4}
\]
6. **Find the Roots:**
- Positive Root:
\[
x = \frac{-7 + 9}{4} = \frac{2}{4} = \frac{1}{2}
\]
- Negative Root:
\[
x = \frac{-7 - 9}{4} = \frac{-16}{4} = -4
\]
**Conclusion:**
The solutions to the equation \( x(2x + 7) = 4 \) are \( x = \frac{1}{2} \) and \( x = -4 \).
Expert Solution
Step 1
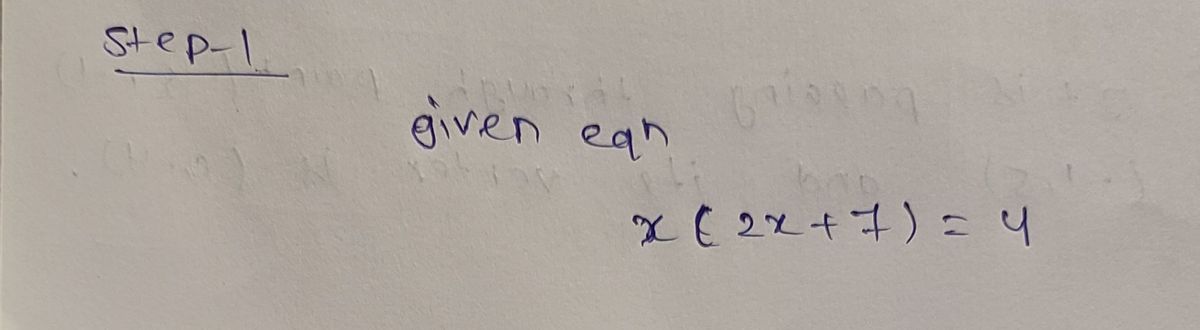
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning