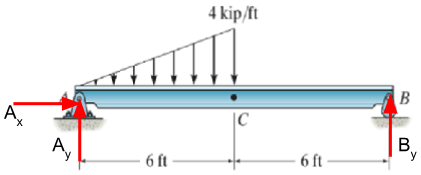
3. Determine the Determine the reactions at A and B. 6 ft 4 kip/ft |C 6 ft B
3. Determine the Determine the reactions at A and B. 6 ft 4 kip/ft |C 6 ft B
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
solution?

Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 3:**
**Objective:** Determine the reactions at points A and B.
**Description of Diagram:**
- The diagram illustrates a beam AB which is supported at both ends, A and B.
- The beam is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of 4 kip/ft acting downward over the entire span.
- The total length of the beam is 12 feet, divided into two segments: 6 feet from A to C, and 6 feet from C to B.
**Visual Elements:**
- Arrows pointing downward indicate the direction of the load applied to the beam.
- Points A and B are the supports where reactions need to be determined. A is a pin support, and B is a roller support.
- The load distribution is consistent, depicted as a series of vertical arrows along the beam from point A to point B.
**Analysis Required:**
- Calculate the reaction forces at the supports (A and B) by applying equilibrium equations.
- Consider the beam as a static system to apply the principles of static equilibrium for solving reaction forces.
This problem involves concepts such as uniformly distributed loads, reaction calculations, and static equilibrium in structures.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Introducing Given data
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning