Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
I appreciate any help I can get :)
![**Problem Statement**
**Objective:** Use the definition of the derivative to find \( f'(x) \) for \( f(x) = \frac{3}{x} \).
In this problem, we start with the function \( f(x) = \frac{3}{x} \) and aim to find its derivative \( f'(x) \) using the fundamental definition of the derivative.
**Definition of the Derivative:**
The derivative of a function \( f(x) \) at any point \( x \) is given by:
\[ f'(x) = \lim_{{h \to 0}} \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h}. \]
**Application of the Definition:**
To find \( f'(x) \) for \( f(x) = \frac{3}{x} \):
1. Start by substituting \( f(x) = \frac{3}{x} \) into the definition of the derivative.
2. Evaluate the limit:
\[ f'(x) = \lim_{{h \to 0}} \frac{\frac{3}{x+h} - \frac{3}{x}}{h}. \]
Breakdown the expression step by step and simplify to find the derivative.
This problem reinforces understanding of the derivative's definition and facilitates practice in algebraic manipulation to simplify limits.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F0058e8ef-7ddd-48c1-a920-2da8be9ae57b%2F6ef4e649-89eb-4a49-97df-c069c5d9c477%2Fy6qspnw.png&w=3840&q=75)
Given:
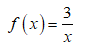
Using definition of derivative, we know:
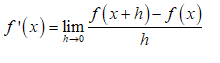
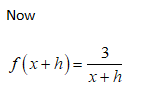
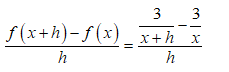
Simplifying above expression:
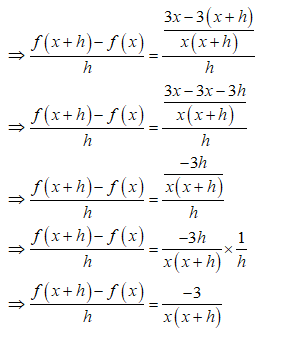
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 7 images









