Calculus For The Life Sciences
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780321964038
Author:GREENWELL, Raymond N., RITCHEY, Nathan P., Lial, Margaret L.
Publisher:GREENWELL, Raymond N., RITCHEY, Nathan P., Lial, Margaret L.
Chapter7: Integration
Section7.3: Area And The Definite Integral
Problem 1E: Explain the difference between an indefinite integral and a definite integral.
Related questions
Question
Evaluate the
![The given image depicts an improper integral from calculus, which is expressed as follows:
\[ \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2} \, dx \]
This integral is evaluated over the entire real line, from negative infinity to positive infinity, and represents the area under the curve of the function \(\frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2}\).
To solve this integral, one might use techniques such as symmetry of the integrand, properties of definite integrals, or advanced integration techniques like residue theorem from complex analysis, depending on the level of calculus knowledge of the student.
Here are possible steps to address the solution:
1. **Symmetry Consideration:** Notice that the integrand \(\frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2}\) is an odd function since \(\frac{2(-x)}{((-x)^2 + 1)^2} = -\frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2}\).
2. **Odd Function Integral Property:** The integral of an odd function over a symmetric interval about the origin is zero. Therefore:
\[ \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2} \, dx = 0 \]
Thus, the value of the given integral is \(0\).
The visualization of the problem or additional supporting graphs can further assist in understanding these concepts, although none are provided in the given image.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F790e387a-579c-4b02-b6cb-cbab761f0d7e%2F2bddc10f-c403-44e3-abb3-021cb3853a43%2Fotk1u19.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:The given image depicts an improper integral from calculus, which is expressed as follows:
\[ \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2} \, dx \]
This integral is evaluated over the entire real line, from negative infinity to positive infinity, and represents the area under the curve of the function \(\frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2}\).
To solve this integral, one might use techniques such as symmetry of the integrand, properties of definite integrals, or advanced integration techniques like residue theorem from complex analysis, depending on the level of calculus knowledge of the student.
Here are possible steps to address the solution:
1. **Symmetry Consideration:** Notice that the integrand \(\frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2}\) is an odd function since \(\frac{2(-x)}{((-x)^2 + 1)^2} = -\frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2}\).
2. **Odd Function Integral Property:** The integral of an odd function over a symmetric interval about the origin is zero. Therefore:
\[ \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{2x}{(x^2 + 1)^2} \, dx = 0 \]
Thus, the value of the given integral is \(0\).
The visualization of the problem or additional supporting graphs can further assist in understanding these concepts, although none are provided in the given image.
Expert Solution
Step 1
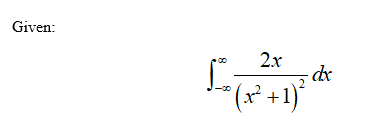
Step 2
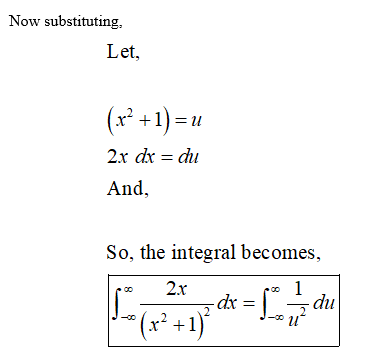
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus For The Life Sciences
Calculus
ISBN:
9780321964038
Author:
GREENWELL, Raymond N., RITCHEY, Nathan P., Lial, Margaret L.
Publisher:
Pearson Addison Wesley,

Calculus For The Life Sciences
Calculus
ISBN:
9780321964038
Author:
GREENWELL, Raymond N., RITCHEY, Nathan P., Lial, Margaret L.
Publisher:
Pearson Addison Wesley,