28. Assume that the following molecule is planar. Use the Frost method to explain whether it is aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. In your Frost diagram, fill in all pi electrons and label the HOMO and the LUMO.
Bond Parameters
Many factors decide the covalent bonding between atoms. Some of the bond parameters are bond angle, bond order, enthalpy, bond length, etc. These parameters decide what kind of bond will form in atoms. Hence it is crucial to understand these parameters in detail and understand how changing these parameters affects the kind of bonding or various characteristics.
Bond Dissociation Energy
The tendency of an atom to attract an electron is known as its electronegativity.

Frost method is a useful method for drawing energy levels in cyclic Pi systems.
In this method a circle is inscribed with polygon with one vertex pointing down.
The vertices represent energy levels with appropriate energies.
Vertices below the half way mark of the circle are considered as bonding orbitals.
Vertices above the half way mark of the circle are considered as antibonding orbitals.
Vertices that are exactly on the middle of the circle are considered as nonbonding orbitals.
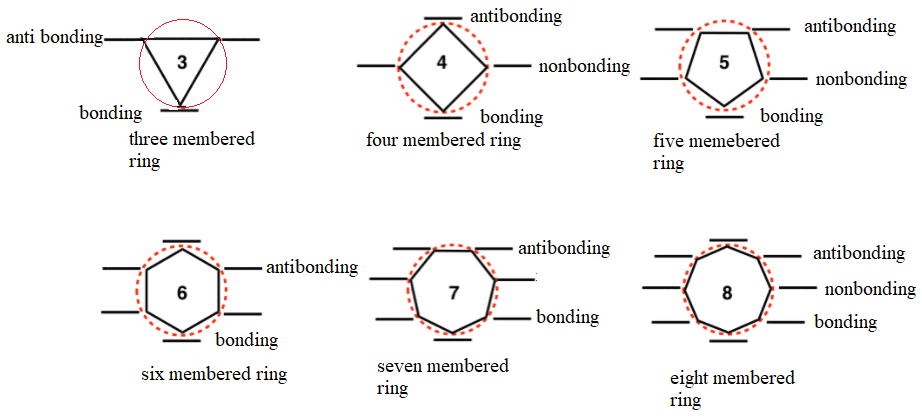
To draw molecular orbitals of a cyclic pi system, draw a suitable polygon with vertex down then, fill it up with electrons.
If electrons are only occupied bonding molecular orbitals then, it is aromatic.
If electrons are present in antibonding molecular orbitals then it is antiaromatic.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images









