22 5 A (1 122 202
Find the current i and the voltage VA from given circuit

From the circuit, the 5Ω resistor is connected in parallel with 20Ω resistor and the parallel combination of 5Ω resistor and 20Ω resistor is in series with 2Ω resistor. The complete combination 5Ω resistor, 20Ω resistor and 2Ω resistor is parallel with 12Ω resistor. The current supplied to the parallel combination 12Ω resistor and combination 5Ω resistor, 20Ω resistor and 2Ω resistor is the current from the current source.
Thus, the complete resistance (R1) of the combination of 5Ω resistor, 20Ω resistor and 2Ω resistor is given by:
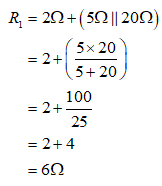
To calculate the current flowing in complete resistance (I1), apply current division rule between 12Ω resistor and R1:
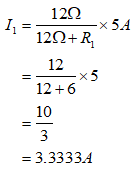
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images









