2.5.1 The probability function of a random variable Y is given by p(i) = ,i = 0, 1, 2, positive value and c is a constant. (a) Find c. (b) Find P(Y=0). (c) Find P(Y> 2). where is a known
2.5.1 The probability function of a random variable Y is given by p(i) = ,i = 0, 1, 2, positive value and c is a constant. (a) Find c. (b) Find P(Y=0). (c) Find P(Y> 2). where is a known
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:2.5.1 The probability function of a random variable Y is given by p(i) == 0, 1, 2,
positive value and c is a constant.
(a) Find c.
(b) Find P(Y=0).
(c) Find P(Y> 2).
2.5.2. Find k so that the function given by
where is a known
Expert Solution
Step 1
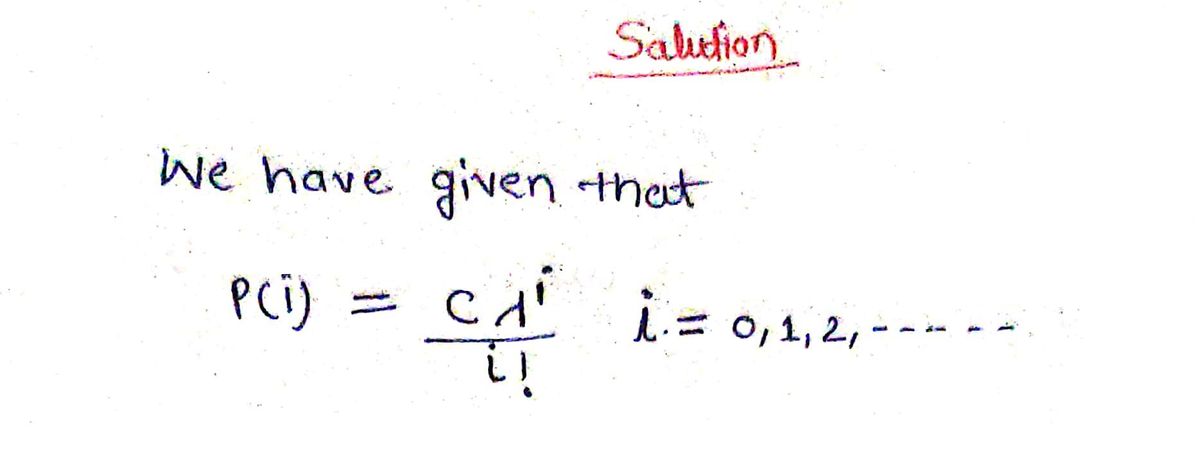
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
