2. Using the reaction mixture in Problem 1, a student found that it took 510 seconds for the color of the 1₂ to disappear. a. What was the rate of the reaction? Hint: First find the initial concentration of I₂ in the reaction mix- ture, [1₂]o. Then use Equation 5. rate= rate = M/sec b. Given the rate from Part (a), and the initial concentrations of acetone, H* ion, and I₂ in the reaction mixture, write Equation 3 as it would apply to the mixture.
2. Using the reaction mixture in Problem 1, a student found that it took 510 seconds for the color of the 1₂ to disappear. a. What was the rate of the reaction? Hint: First find the initial concentration of I₂ in the reaction mix- ture, [1₂]o. Then use Equation 5. rate= rate = M/sec b. Given the rate from Part (a), and the initial concentrations of acetone, H* ion, and I₂ in the reaction mixture, write Equation 3 as it would apply to the mixture.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
Please answer 2b highlighted. Explain
![1. In a reaction involving the iodination of acetone, the following volumes were used to make up the reac-
tion mixture:
a.
How many moles of acetone were in the reaction mixture? Recall that, for a component A, moles
A = MAX V, where MA is the molarity of A and V is the volume in liters of the solution of A that
was used.
5 mL 4.0 M acetone + 10 mL 1.0 M HCl + 10 mL 0.0050 M I₂ + 25 mL H₂O
M₁ =
b. What was the molarity of acetone in the reaction mixture? The volume of the mixture was 50 mL,
0.050 L, and the number of moles of acetone was found in Part (a). Again,
moles of A
V of soln. in liters
moles acetone
c. How could you double the molarity of the acetone in the reaction mixture, keeping the total volume
at 50 mL and keeping the same concentrations of H+ ion and I₂ as in the original mixture?
rate =
2. Using the reaction mixture in Problem 1, a student found that it took 510 seconds for the color of the 1₂ to
disappear.
M acetone
a. What was the rate of the reaction? Hint: First find the initial concentration of I₂ in the reaction mix-
ture, [1₂]o. Then use Equation 5.
rate =
C. What are the unknowns that remain in the equation in Part (b)?
b. Given the rate from Part (a), and the initial concentrations of acetone, H* ion, and I₂ in the reaction
mixture, write Equation 3 as it would apply to the mixture.
M/sec](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F21b2424c-a4ba-45d0-aa84-edf812370fbb%2F81e4bb8d-8979-4a56-a615-4714f22655f6%2Fucezuxh_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:1. In a reaction involving the iodination of acetone, the following volumes were used to make up the reac-
tion mixture:
a.
How many moles of acetone were in the reaction mixture? Recall that, for a component A, moles
A = MAX V, where MA is the molarity of A and V is the volume in liters of the solution of A that
was used.
5 mL 4.0 M acetone + 10 mL 1.0 M HCl + 10 mL 0.0050 M I₂ + 25 mL H₂O
M₁ =
b. What was the molarity of acetone in the reaction mixture? The volume of the mixture was 50 mL,
0.050 L, and the number of moles of acetone was found in Part (a). Again,
moles of A
V of soln. in liters
moles acetone
c. How could you double the molarity of the acetone in the reaction mixture, keeping the total volume
at 50 mL and keeping the same concentrations of H+ ion and I₂ as in the original mixture?
rate =
2. Using the reaction mixture in Problem 1, a student found that it took 510 seconds for the color of the 1₂ to
disappear.
M acetone
a. What was the rate of the reaction? Hint: First find the initial concentration of I₂ in the reaction mix-
ture, [1₂]o. Then use Equation 5.
rate =
C. What are the unknowns that remain in the equation in Part (b)?
b. Given the rate from Part (a), and the initial concentrations of acetone, H* ion, and I₂ in the reaction
mixture, write Equation 3 as it would apply to the mixture.
M/sec
Expert Solution
Step 1
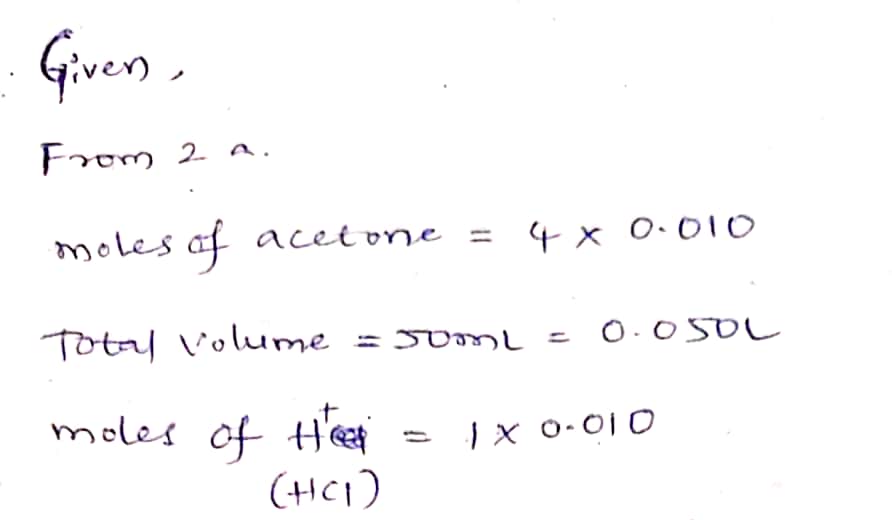
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY