2. Use the tree diagram to find the probability of selecting different iPhones. You have: 2 phones to choose from: o iPhone 11 and iPhone 12, 3 colors: o silver, o black, and o gold, 2 amounts of storage o 64GB and 128GB. iPhone 11 iPhone 12 black silver gold black silver gold 128 256 128 256| 128 256 128 GB 256 128 256 128 256 GB GB GB GB GB GB GB GB GB GB GB Show you work in the space provided. a. P(black iPhone) = ь. Р(128GB iPhone) - P (iPhone 11) =
2. Use the tree diagram to find the probability of selecting different iPhones. You have: 2 phones to choose from: o iPhone 11 and iPhone 12, 3 colors: o silver, o black, and o gold, 2 amounts of storage o 64GB and 128GB. iPhone 11 iPhone 12 black silver gold black silver gold 128 256 128 256| 128 256 128 GB 256 128 256 128 256 GB GB GB GB GB GB GB GB GB GB GB Show you work in the space provided. a. P(black iPhone) = ь. Р(128GB iPhone) - P (iPhone 11) =
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:2. Use the tree diagram to find the probability of selecting different iPhones.
You have:
2 phones to choose from:
o iPhone 11 and iPhone 12,
3 colors:
o silver,
o black, and
o gold,
2 amounts of storage
o 64GB and 128GB.
iPhone 11
iPhone 12
black
silver
gold
black
silver
gold
128 256 128 256
256 128 256 128 256
GB
128 256 128
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
GB
Show you work in the space provided.
a. P (black iPhone) =
b. Р(128GB iPhone) -
P (iPhone 11) =
с.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Event: In probability theory, an event is an outcome or a set of outcomes of a random experiment to which a probability is assigned. A single outcome is an element of a sample space and different events in a random experiment are generally not equally likely, since they may include very different groups of outcomes.
Classical Definition of Probability: If there are n mutually exclusive, exhaustive and equally likely outcomes of a random experiment and n(A) of them are favorable to the occurrence of event A, then according to the Classical definition of Probability, the probability of A, denoted by P(A), is defined by the ratio of n(A) and n.
It is given by the formula,
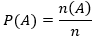
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
