12. An Organic Compound with the Following Spectra (you need to determine what atoms are present) Wavelength (am) 2,5 2,6 27 28 29 3 4000 3800 3600 3400 3200 3000 2800 2600 2400 2200 2000 I800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 Wavenumber (em) %3D
12. An Organic Compound with the Following Spectra (you need to determine what atoms are present) Wavelength (am) 2,5 2,6 27 28 29 3 4000 3800 3600 3400 3200 3000 2800 2600 2400 2200 2000 I800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 Wavenumber (em) %3D
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
100%
Please help me

Transcribed Image Text:12. An Organic Compound with the Following Spectra (you need to
determine what atoms are present)
2,5 2,6 2,7 28 29 3
3,5
Manclength (am)
IS 16
4.5
10
%3D
12
13
14
4000 3800 3600
3400
3200 3000 2800
2600
2400
2200
2000
1800
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
600
Wavenumber (em
100
44
72
50
20
40
60
80
100
mlz
3H,t
2H,m
1H, t
2H,m
10
PPM
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
pom
Proposed Structure:
Degree of Unsaturation:
Relative abundance

Transcribed Image Text:SPECTROSCOPY DRY LAB
General Formula to calculate the degree of unsaturation:
#C atoms - (#H atoms/2) + 1
Example: Benzene (C6H6) 6 - (6/2) + 1 = 4
Rules for calculating unsaturation with organic compounds that contain heteroatoms
(halogen, O, S, N)
Rule 1) Replace any halogens with hydrogens
Example: CH3B change to CH4 and then calculate 1- (4/2) + 1 = 0
Rule 2) Ignore any O or S atoms in the compound
Example: Phenol (C6H5OH) calculate for C6H6 6- (6/2) + 1 = 4
Rule 3) Subtract a H for every Nitrogen present
Example: Aniline (C6H5NH2) calculate for C6H6 6- (6/2) + 1 = 4
For the following problems given spectral data and the chemical formula:
1) Determine the degree of unsatuaration using the unsaturation rules above and list it in the
appropriate box:
2) Label important absorption bands directly on the IR spectra
3) Identify and label all signals directly on the 1H NMR and or 13C NMR spectra (make sure to
use Ha, Hb, Ca, Cb, etc...
Remember TMS shows up as a singlet at 0 ppm for both the 1H and the 13C NMR
CDCI3 (solvent) sometimes shows up as a triplet around 77pm in a 1°C NMR
4) Propose a structure for the compound that matches 1-3 above (If your structure has more
than four degrees of unsaturation it's quite likely to have an aromatic ring). Draw the
SKELETAL structure in the proposed structure box.
Expert Solution
Description
The structure I have elucidated as per the given experimental data is butanal.
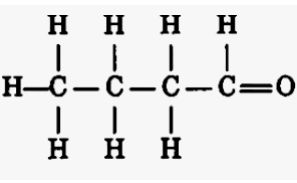
C4H8O
That is the C=O double bond.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY