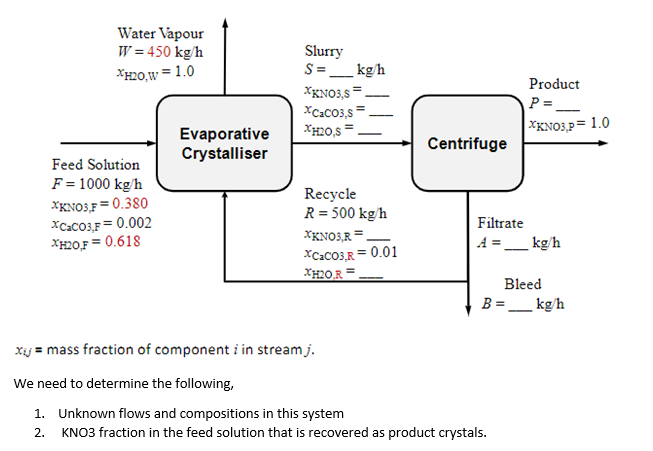
1000 kg/h of an aqueous feed solution containing 38 wt.% potassium nitrate (KNO3) and 0.2 wt.% CaCO3 (the rest is water) is crystallised in an evaporative crystalliser. 450 kg/h of water vapour are evaporated from the crystalliser to create a super‐saturated solution which then causes crystals to form and grow. The product crystal slurry is then fed to a centrifuge where perfectly dry KNO3 crystals are recovered.1 The filtrate solution (which still contains some dissolved KNO3 as well as dissolved CaCO3) is recycled back to the crystalliser. However, a bleed (purge) stream is split off and removed in order to keep the concentration of CaCO3 in the return solution from climbing above 1 wt.% (in order to prevent crystallisation of CaCO3 when its concentration builds up too high). Once this bleed is removed, the remaining 500 kg/h of solution is recycled. See diagram. Determine: 1. Unknown flows and compositions in this system. 2. KNO3 fraction in the feed solution that is recovered as product crystals.
1000 kg/h of an aqueous feed solution containing 38 wt.% potassium nitrate (KNO3) and 0.2 wt.%
CaCO3 (the rest is water) is crystallised in an evaporative crystalliser. 450 kg/h of water vapour are
evaporated from the crystalliser to create a super‐saturated solution which then causes crystals to
form and grow. The product crystal slurry is then fed to a centrifuge where perfectly dry KNO3
crystals are recovered.1 The filtrate solution (which still contains some dissolved KNO3 as well as
dissolved CaCO3) is recycled back to the crystalliser. However, a bleed (purge) stream is split off and
removed in order to keep the concentration of CaCO3 in the return solution from climbing above 1
wt.% (in order to prevent crystallisation of CaCO3 when its concentration builds up too high). Once
this bleed is removed, the remaining 500 kg/h of solution is recycled. See diagram.
Determine:
1. Unknown flows and compositions in this system.
2. KNO3 fraction in the feed solution that is recovered as product crystals.

Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 9 images









